order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
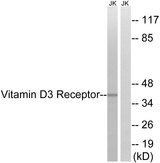
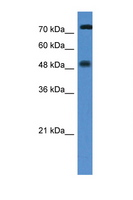
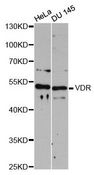
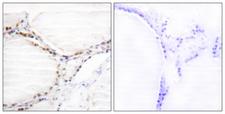
Vitamin D Receptor / VDR
vitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor
The vitamin D receptor, a NR1 Thyroid Hormone-Like Receptor, is activated by calcitriol, the active hormonal form of vitamin D. The activated receptor binds DNA at a specific vitamin D-responsive element and promotes transcription of vitamin D target genes such as osteocalcin, the most abundant noncollagenous protein in bone. The vitamin D receptor affects growth, bone formation, and female reproduction. For example, this receptor modulates the growth and differentiation of keratinocytes and mediates the beneficial effects of vitamin D on psoriatic skin. It also inhibits hormone secretion by and proliferation of parathyroid cells. The vitamin D receptor functions either as a homodimer or as a heterodimer of vitamin D and retinoid acid X receptor subunits. Inactivation of the receptor leads to hypocalcemia and Rickets-alopecia syndrome. Recently, the vitamin D receptor has been shown to function as a receptor for the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid (LCA), which is hepatotoxic and a potential enteric carcinogen. Activation of VDR by LCA or vitamin D induced expression in vivo of CYP3A, a cytochrome P450 enzyme that detoxifies LCA in the liver and intestine. An alternatively spliced vitamin D receptor that has an altered ligand-binding domain has been isolated from rats.
| Gene Name: | vitamin D (1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3) receptor |
| Family/Subfamily: | NHR , NR1 Thyroid hormone-like |
| Synonyms: | VDR, NR1I1, Vitamin D3 receptor, Vitamin D receptor |
| Target Sequences: | NM_000376 NP_000367.1 P11473 |
Publications (3)
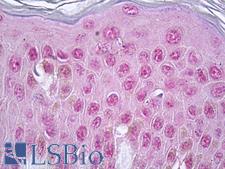
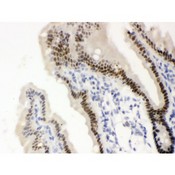
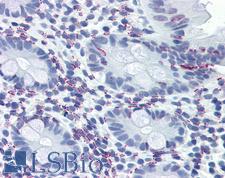
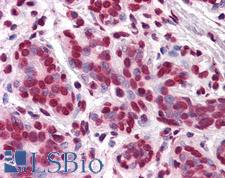
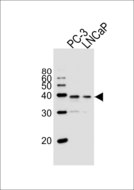
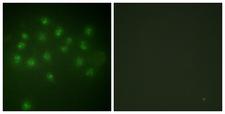
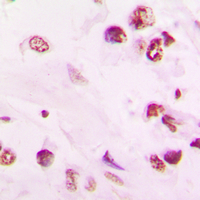
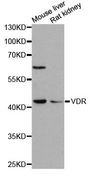


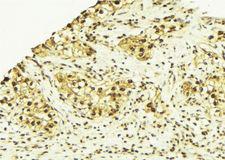


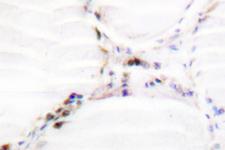
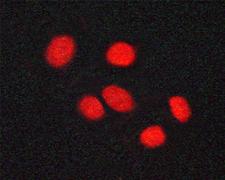
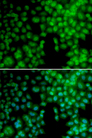
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.










