Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM GLP1R / GLP-1 Receptor Antibodies
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R) is a receptor for glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP1). It is involved in insulin synthesis and release, blood glucose homeostasis, appetite control, memory and learning, as well as control of breathing and heart rate. Stimulation of GLP1R by endogenous hormone induces multiple complementary mechanisms, which together result in a lowering of circulating blood glucose levels. Desensitization of GLP1R on pancreatic beta-cells is one of the causes of non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). In immunohistochemistry, GLP1R has highest membranous positivity on pancreatic beta cells, it is expressed on neurons in the brain and nervous system, and it is also found in the stomach, salivary gland, heart muscle, gallbladder, salivary gland, duodenum and at low levels in a few other tissues.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
GLP1R / GLP-1 Receptor
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(2)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
IF
(2)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
GPCR Database Antibodies
(2)
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
N-Terminus
(2)
Publications
Yes
(2)

Neuroscience
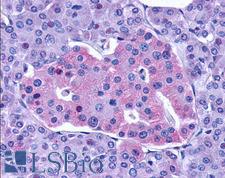
GLP1R / GLP-1 Receptor Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (N-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460

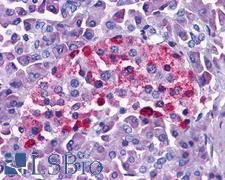
Neuroscience
GLP1R / GLP-1 Receptor Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (N-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IF, IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











