Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CD36 Antibodies
CD36 (also known as platelet glycoprotein 4) is a multifunctional membrane-bound glycoprotein receptor for a broad range of ligands. It is a scavenger receptor for proteins such as thrombospondin, collagen, fibronectin, and amyloid-beta as well as oxidized phospholipids, apoptotic cells, and microbial pathogens, acting to internalize receptor-ligand complexes. It is implicated in platelet disorders, atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and Alzheimer disease. CD36 is found on mononuclear phagocytes, platelets, adipocytes, megakaryocytes, erythroid precursors, myocytes, hepatocytes, endothelial cells, and some epithelia. It has also been reported to be expressed in some diseased tissues such as the brain in Alzheimer disease, leukemias, myxoid liposarcoma, and squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix.
References: Sci Signal. 2009;2(72):re3. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.272re3; Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2010;121:206-220. PMID: 20697562; Am J Pathol. 2002;160(1):101-112. PMID: 11786404; Mod Pathol. 1998;11(12):1211-1221. PMID: 9872654; Hum Pathol. 1994;25(1):73-79. PMID: 7508885; Am J Clin Pathol. 1995;103(1):20-26. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/103.1.20;
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
CD36
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(1)
SWB
(1)
Host
rabbit
(3)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(3)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Publications
No
(3)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
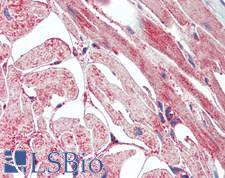
CD36 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
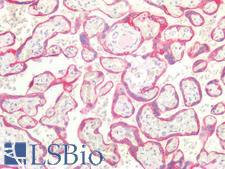
CD36 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
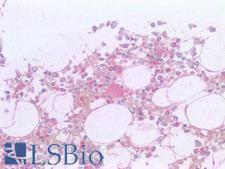
CD36 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P, SWB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











