Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
| Catalog Number | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|
| LS-C188624-0.2 | 0.2 mg (1 mg/ml) | $508 |
Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human APOE / Apolipoprotein E Antibody (clone WUE‑4, WB) LS‑C188624
Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human APOE / Apolipoprotein E Antibody (clone WUE‑4, WB) LS‑C188624
Antibody:
APOE / Apolipoprotein E Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (WUE-4) Antibody
Application:
WB, ELISA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Other formats:
Toll Free North America
 (800) 227-6666
(800) 227-6666
For Research Use Only
Overview
Antibody:
APOE / Apolipoprotein E Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (WUE-4) Antibody
Application:
WB, ELISA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Other formats:
Specifications
Description
Apolipoprotein E antibody LS-C188624 is an unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody to human Apolipoprotein E (APOE). Validated for ELISA and WB.
Target
Human APOE / Apolipoprotein E
Synonyms
APOE | AD2 | Apo-E | Apolipoprotein E3 | Apolipoprotein E | LDLCQ5 | LPG
Host
Mouse
Reactivity
Human
(tested or 100% immunogen sequence identity)
Clonality
IgG1
Monoclonal
Clone
WUE-4
Conjugations
Unconjugated.
Also available conjugated with Biotin.
Purification
Protein G purified
Modifications
Unmodified.
Also available Low Endotoxin.
Immunogen
Purified ApoHDL fraction.
Specificity
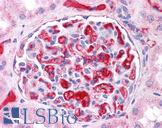
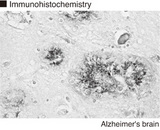
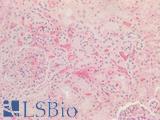
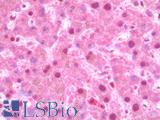
Recognizes an epitope within amino acids 140-160 of human apolipoprotein E (Apo-E), a major component of very low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs). Apo-E is the principle apolipoprotein in the central nervous system, and is secreted by most organs into the plasma, playing a vital role in the binding, internalization and catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein constituents. Apo-E acts as a ligand for both the specific apo-E receptor (chylomicron remnant) of hepatic tissues, and the apoB, E (LDL) receptor. Three isoforms of Apo-E have been identified, ApoE2, E3 and E4, and have been linked with various disorders. ApoE2 has been shown to bind LPL receptors with low affinity, resulting in increased plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and thereby an increased risk in cardiovascular disorders. ApoE4 is a known high risk factor for Alzheimer's disease, and in particular late onset Alzheimer disease 2 (AD2), whilst ApoE3 is the most common isoform, and considered the normal/natural Apo-E genotype. Clone WUE-4 has been shown to inhibit Apo-E mediated binding of lipoproteins to the apoB, E cell receptor.
Applications
- Western blot
- ELISA (1:100 - 1:1000)
Presentation
PBS, 0.09% Sodium Azide
Storage
Store at 4°C or at -20°C. Store undiluted. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Microcentrifugation recommended if solution contains precipitate.
Restrictions
For research use only. Intended for use by laboratory professionals.
About APOE / Apolipoprotein E
Publications (0)
Customer Reviews (0)
Featured Products
Species:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Western blot
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, Western blot, Immunoprecipitation
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC - Paraffin, Western blot, Peptide Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Species:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Immunofluorescence, Western blot, ELISA
Species:
Human, Mouse
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Western blot
Request SDS/MSDS
To request an SDS/MSDS form for this product, please contact our Technical Support department at:
Technical.Support@LSBio.com
Requested From: United States
Date Requested: 3/4/2025
Date Requested: 3/4/2025