order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
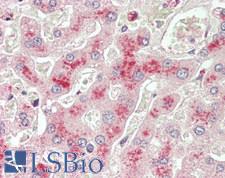
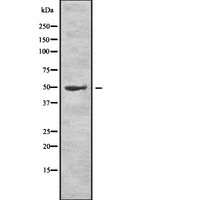
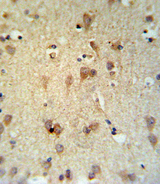
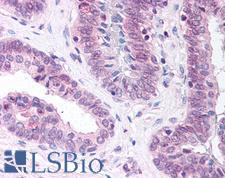
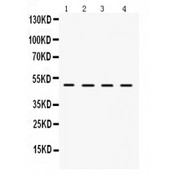
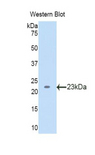
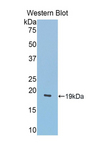
LCAT
lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase
Central enzyme in the extracellular metabolism of plasma lipoproteins. Synthesized mainly in the liver and secreted into plasma where it converts cholesterol and phosphatidylcholines (lecithins) to cholesteryl esters and lysophosphatidylcholines on the surface of high and low density lipoproteins (HDLs and LDLs). The cholesterol ester is then transported back to the liver. Has a preference for plasma 16:0-18:2 or 18:O-18:2 phosphatidylcholines. Also produced in the brain by primary astrocytes, and esterifies free cholesterol on nascent APOE-containing lipoproteins secreted from glia and influences cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) APOE- and APOA1 levels. Together with APOE and the cholesterol transporter ABCA1, plays a key role in the maturation of glial-derived, nascent lipoproteins. Required for remodeling high-density lipoprotein particles into their spherical forms.
| Gene Name: | lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase |
| Synonyms: | LCAT |
| Target Sequences: | NM_000229 NP_000220.1 P04180 |
Publications (8)
![LCAT Antibody - Immunofluorescence of monoclonal antibody to LCAT on HeLa cell . [antibody concentration 10 ug/ml]](https://lsbio-7d62.kxcdn.com/image2/lcat-antibody-clone-4a9-ls-c197605/145536_4947644.jpg)





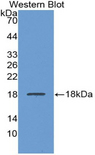
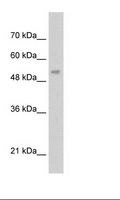
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.











