order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
CD274 / B7-H1 / PD-L1
CD274 molecule
CD274, also known as B7-H1 and PD-L1, a cell surface glycoprotein, is a member of the B7 family of co-stimulatory molecules. CD274 is expressed constitutively on macrophages and dendritic cells, and is induced on activated T-cells, B-cells, endothelial cells and epithelial cells in response to interferons. CD274 has dual functions: inhibition of activated effector T cells and co-stimulation of naïve T cells. It inhibits proliferation of activated T cells via ligation to the co-inhibitory molecule CD279 (programmed death-1; PD-1) leading to the secretion of the regulatory cytokine interleukin-10. Expression of CD274 in tumor cells is considered to be prognostic in many types of human malignancies, including colon cancer and renal cell carcinoma.
| Gene Name: | CD274 molecule |
| Synonyms: | CD274, B7-H, B7 homolog 1, B7-H1, B7H1, CD274 molecule, CD274 antigen, PDCD1 ligand 1, PDL1, PD-L1, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1, Programmed death ligand 1 |
| Target Sequences: | NM_014143 NP_054862.1 Q9NZQ7 |
Publications (19)

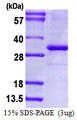
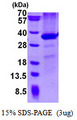
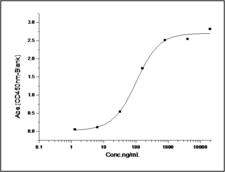
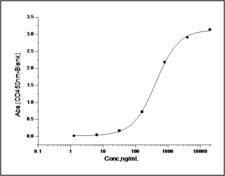

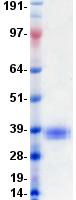
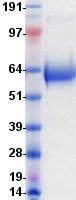
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.









