Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM TLR4 Antibodies
TLR4 (Toll-like receptor 4) is a transmembrane protein involved in the immune response, inflammation, and cytokine secretion. TLR4 activates the NF-kappa-B (NFKB) and po-Interleukin-1 beta (IL1B) pathways in the brain and is thus relevant to neuro-inflammation and pathological neurodegenerative conditions. It has been found to positively regulate the proliferation of Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system, it is upregulated in injured nerves, and it is involved in inflammation in brain injury. TLR4 is also expressed in astrocytes and neurons as part of the immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Likewise, mutations in TLR4 lead to susceptibility to infections by gram-negative bacteria. Additionally, TLR4 is expressed on many cancer cells, where it may increase proliferative capacity and resistance to therapies. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, TLR4 has highest cytoplasmic positivity in immune cells, in the placenta, and in microglia and neurons in the brain.
References: Archives of Internal Medicine. 162 (9): 1028–32,PMID: 11996613; Cytokine. 89: 127–135, PMID: 26854213; Sci Rep. 2018; 8: 11179, PMID: 30046125; Front Immunol. 2019 May 10;10:1000, PMID: 31134076; Front Immunol. 2019 May 10;10:1000, PMID: 31134076
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
TLR4
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(1)
Flo
(1)
ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG2b,k
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(2)
Clone
76B357.1
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
Internal
(1)
aa100-200
(1)
Publications
No
(2)
Yes
(1)

Neuroscience
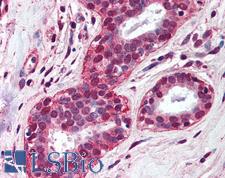
TLR4 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (aa100-200) (76B357.1) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

Neuroscience
Fast Shipping
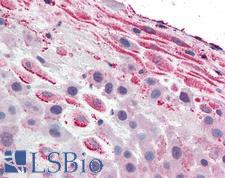
TLR4 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Neuroscience
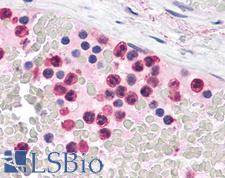
TLR4 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results










