Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM SLC2A1 / GLUT-1 Antibodies
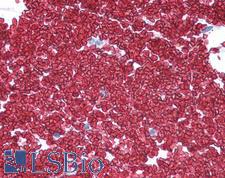
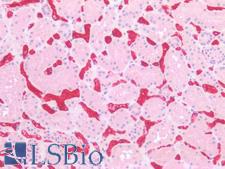
SLC2A1 (also known as GLUT1) is a facilitative glucose transporter protein involved in constitutive or basal glucose uptake. It is capable of transporting a wide range of aldoses, including both pentoses and hexoses, across the plasma membrane. SLC2A1 mutations lead to GLUT1 deficiency syndrome 1 and 2, dystonia, idiopathic generalized epilepsy and stomatin-deficient cryohydrocytosis. GLUT1 is also relevant to Alzheimer’s disease and neurodegenerative disorders, as lower levels of GLUT1 have been found to contribute to vascular degeneration, diminished neuronal activity, reductions in blood flow and blood-brain barrier degeneration. In immunohistochemistry, SLC2A1 has highest cytoplasmic positivity in trophoblasts, erythrocytes, and endothelial cells in the blood-brain barrier, and also has lower levels of staining in most other tissues.
References: Annual Review of Nutrition. 16: 235–56, PMID: 8839927; Nucleic Acids Research. 45 (D1): D158–D169. January 2017, PMID: 27899622; Pflügers Archiv. 2004. 447 (5): 480–9, PMID: 12750891; Nat Neurosci. 2015 Apr;18(4):521-530, PMID: 25730668;
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
SLC2A1 / GLUT-1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(2)
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Concentrated
(1)
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
Cancer Pathology
SLC2A1 / GLUT-1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Rat, Human
IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$545

Neuroscience
Cancer Pathology
SLC2A1 / GLUT-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Concentrated) Antibody
Human
IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Unconjugated, Concentrated
0.05 ml/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










