Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM SERPINB5 / Maspin Antibodies
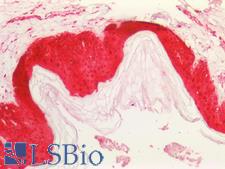
SERPINB5 (maspin) is a serine protease inhibitor regulated by TP53 that has putative tumor suppressor functions. It is involved in mammary gland development via EGFR signaling. In cancer, both the degree of expression and the cellular localization of SERPINB5 correlates with stage and progression in some cancers. For example, SERPINB5 has generally nuclear positivity in normal epithelium, and primarily cytoplasmic localization of SERPINB5 is associated with tumorigenesis in lung, prostate and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cytoplasmic SERPINB5 may be a useful early diagnostic biomarker for the transformation of normal epithelia and Barrett’s esophagus into esophageal adenocarcinoma; overall expression of SERPINB5 appears to decrease with stage and cellular distribution trends from nuclear to cytoplasmic alongside progression. SERPINB5 expression is lost in invasive subtypes, and predominantly cytoplasmic expression may be indicative of pre-neoplastic lesions with a greater risk of progression to adenocarcinoma. Dzinic et al have indicated that SERPINB5 may only have tumor suppressive functions while localized to the nucleus, where it suppresses HDAC1 suppression, plays a role in chromatin folding and contributes to genetic stability. Predominantly cytoplasmic expression and absence in the nucleus may thus lead to an increase in DNA mutations and ultimately promote tumor cell survival. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, SERPINB5 has both cytoplasmic and nuclear positivity in the esophagus, prostate, skin, intestine, lung, cerebral cortex, thymus, testis and tongue.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804; Neurol Res. 2010 Apr;32(3):303-8, PMID: 19909580; Science. 263 (5146): 526–9, PMID: 8290962; PLoS One. 2016; 11(7): e0159856, PMID: 27447178; PLoS One. 2019 Apr 19;14(4):e0215089, PMID: 31002675; Cancer Res. 2006 Sep 15;66(18):9323-9, PMID: 16982778
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
SERPINB5 / Maspin
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Application
IHC-P
(1)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Cancer
SERPINB5 / Maspin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$485
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results










