Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM PSAP / Prosaposin Antibodies
PSAP (Prosaposin, SAP1) is a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate saposins A, B, C, and D. Saposins localize to lysosomes where they catabolize glycosphingolipids with short oligosaccharide groups. The precursor exists as both a secretory and integral membrane protein. The secretory prosaposin promotes protective effects in the nervous system by activating G proteins, including GPR37 and GPR37L1. Mutations in PSAP are associated with Gaucher disease and metachromatic leukodystrophy. The protein is expressed in all tissues.
References: Brain Res 2014 1585:1; Am J Med Genet 2009 149A(4):613; Mol Genet Metab 2012 106(3):257
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
PSAP / Prosaposin
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(3)
ELISA
(1)
IP
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(3)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG2a,k
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(2)
Clone
1D1-C12
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
Internal
(1)
aa1-250
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
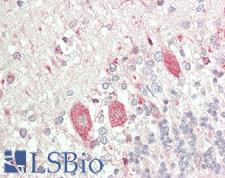
PSAP / Prosaposin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

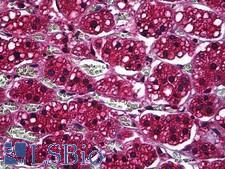
Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PSAP / Prosaposin Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (1D1-C12) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
100 µg/$375

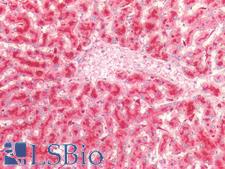
Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PSAP / Prosaposin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa1-250) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results










