Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM NGF Antibodies
NGF (Nerve growth factor) is a neurotrophic protein with important functions in maintaining the integrity and proper function of target neurons in the developing and adult brain. It controls the plasticity, differentiation and proliferation of cholinergic neurons in the nervous system, which are important for cognition. NGF metabolism is altered in Alzheimer’s disease, which leads to neuronal atrophy and a loss of cortical synapses. Several decades of study indicates that NGF has neuro-protective and regenerative characteristics in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and in aging. Delivery of NGF to cholinergic cell bodies in the cortex and hippocampus has been attempted as a means of rehabilitating cholinergic signaling and suppressing cognitive decline. Separately, high NGF levels in the plasma are correlated with recent feelings of romantic love, in part due to its stimulation of adrenocorticotrophic hormone and cortisol release. In immunohistochemistry, NGF has variable levels of secretory, extracellular and cytoplasmic positivity in most tissues throughout the body.
References: Front Neurosci. 2019 Feb 5;13:38, PMID: 30804738; Rev Neurosci. 1994 Jul-Sep;5(3):179-211, PMID: 7889213; Progress in Brain Research. 2004. 146: 111–26,PMID: 14699960; Brain Research. 217 (1): 207–211, PMID: 6114784;
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
NGF
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(3)
Rat
(2)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(3)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(3)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
Internal
(1)
Leu82
(1)
aa33-82
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
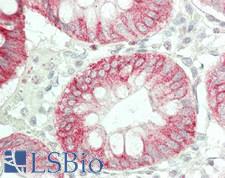
NGF Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Leu82) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Neuroscience
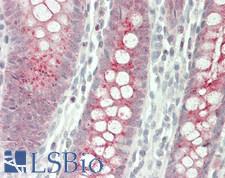
NGF Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Neuroscience
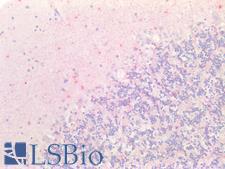
NGF Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa33-82) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results










