Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
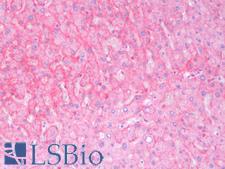
PathPlusTM KRAS Antibodies
KRAS is a RAS/MAPK signaling pathway GTPase that is involved in the control of cell proliferation. It is the most commonly mutated oncogene in human cancers, with a high frequency in carcinomas of the pancreas, colon, and lung. KRAS mutation is commonly associated with poor prognosis and resistance to therapy. The four somatic KRAS mutations with the most frequency in tumors, G12D, G12V, G12C and G13D, are associated with a large number of morphological and regulatory changes and a sudden increase in the rate of cellular proliferation. These mutations are driving events in the formation of invasive carcinomas when combined with the loss of function of a tumor suppressor such as APC. The protein is widely expressed, with cytoplasmic and/or membranous localization.
References: Trends in Cancer 2017 3(10):686; Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2018 8(9):a031435; Stolze, 2015; Pino, 2010; Morkel ,2015
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
KRAS
(1)
Application
IHC-P
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
KRAS Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results










