Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM IDE Antibodies
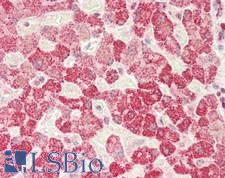
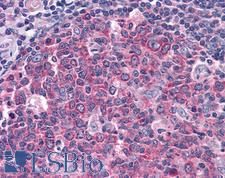
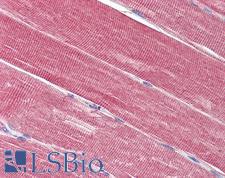
IDE (Insulin-degrading enzye, INSULYSIN) is a zinc metallopeptidase that functions in intracellular signaling by degrading and terminating the activity of a number of peptides including insulin, glucagon, amylin, kallidin, and bradykinin. IDE is involved in regulating the insulin-mediated inhibition of amyloid-beta peptide degradation. A decrease in IDE expression results in a loss in amyloid-beta degradation (and a consequential increase in cerebral accumulations of amyloid-beta) and may contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. IDE dysfunction is correlated with Alzheimer's disease and also with type 2 diabetes mellitus, but IDE mutations have not been clearly demonstrated to cause either. In immunohistochemistry, IDE has primarily cytoplasmic positivity with some extracellular or membranous localization, and it is found in all tissues throughout the body.
References: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 1;100(7):4162-7, PMID: 12634421; Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2019 Dec; 11: 392–404, PMID: 31193223; Journal of Biomedicine & Biotechnology. 2006 (3): 58406, PMID: 17047308.
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
IDE
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Bat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Hamster
(1)
Horse
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Pig
(1)
Rabbit
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(2)
Host
rabbit
(1)
mouse
(1)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(2)
Clone
3H4
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
aa222-233
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
IDE Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (3H4) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

Neuroscience
IDE Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Neuroscience
IDE Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa222-233) Antibody
Rabbit, Mouse, Dog, Bovine, Rat, Hamster, Pig, Horse, Bat, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results










