Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
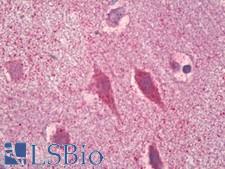
PathPlusTM GRIN1 / NMDAR1 Antibodies
NMDAR1 is a glutamate receptor that plays an essential role in memory and neuronal development. Glutamate receptors are the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the mammalian brain and are activated in a variety of normal neurophysiologic processes. The ion channels activated by glutamate are typically divided into two classes, and those that are sensitive to N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) are designated NMDA receptors (NMDAR). Increased membrane surface expression of the NR1 subunit of this receptor has been associated with synaptic plasticity. It has also been implicated in several disorders of the central nervous system including Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy and ischemic neuronal cell death.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
GRIN1 / NMDAR1
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
WB
(1)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(1)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
aa864-913
(1)
Publications
Yes
(1)

Neuroscience
GRIN1 / NMDAR1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa864-913) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











