Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM FOXC1 Antibodies
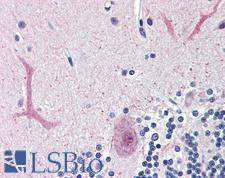
FOXC1 is a forkhead transcription factor involved in embryogenesis, cardiac morphogenesis and ocular development. Inherited mutations in FOXC1 lead to glaucoma, Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome and cerebral small-vessel disease (CSVD), described by increased risk for stroke and progressive cognitive decline. Upregulation of FOXC1 in cancer is common and linked with poor prognosis, as it leads to increased expression of vimentin, N-cadherin and fibronectin and consequently promotes migration and metastasis. In immunohistochemistry, FOXC1 has highest cytoplasmic and nuclear positivity in the central nervous system and salivary gland, and is also moderately expressed in most other tissues throughout the body.
References: Developmental biology. 2006. 421-436. ISBN-10: 0-87893-243-7; Molecular Medicine Reports. 12 (6): 8003–9, PMID: 26461269; Oncogene. 2017 Jul 13;36(28):3957-3963, PMID: 28288141; J Clin Invest. 2014 Nov;124(11):4877-81, PMID: 25250569
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
FOXC1
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Xenopus
(1)
Zebrafish
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
WB
(1)
IF
(1)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
aa541-553
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Neuroscience
FOXC1 Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa541-553) Antibody
Xenopus, Zebrafish, Mouse, Human, Monkey
IF, IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











