Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
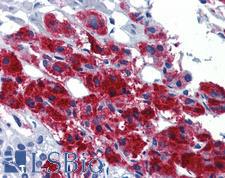
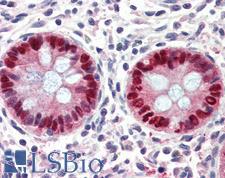
PathPlusTM EGR2 Antibodies
EGR2 (Early growth response protein 2, KROX20) is a transcription factor expressed in migrating neural crest cells and in neural crest-derived cells in the cranial ganglion. It is important for hindbrain development, maintenance of bone architecture, the lymphocyte immune response, regulation of HF cell differentiation, and Schwann cell myelination. EGR2 mutations are correlated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Dejerine-Stotas disease and congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy. Loss of EGR2 expression is believed to lead to male baldness. Furthermore, expression of this protein is associated with Ewing sarcoma. In immunohistochemistry, EGR2 has nuclear positivity in the brain, thyroid and epididymis, and it is also found at variable levels in a number of other tissues including the lung, liver, reproductive tissues, muscle, skin, gastrointestinal tract, and immune tissues.
References: Nature. 337 (6206): 461–4, PMID: 2915691; Nucleic Acids Research. 21 (5): 1087–95, PMID: 8464695; Nature Genetics. 18 (4): 382–4, PMID: 9537424; J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 12; 288(28): 20488–20498, PMID: 23720781; Genes Dev. 2017 Apr 15; 31(8): 744–756, PMID: 28465357
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
EGR2
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Horse
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Pig
(1)
Rabbit
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
aa239-251
(1)
aa397-446
(1)
Publications
No
(1)
Yes
(1)

Neuroscience
EGR2 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa397-446) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Neuroscience
EGR2 Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa239-251) Antibody
Rabbit, Dog, Bovine, Pig, Horse, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











