Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CD6 Antibodies
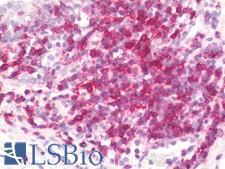
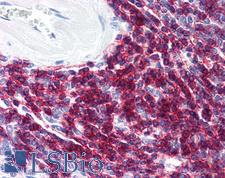
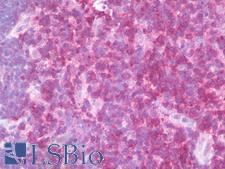
CD6 is a protein found on the outer membrane of T-lymphocytes as well as some other immune cells. The encoded protein contains three scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domains and a binding site for an activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule. CD6 is important for continuation of T cell activation, and mutations in the gene are associated with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. CD6 has been found to be overexpressed in the inflamed mucosa of individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), where it is thought to increase intestinal immune responses. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, CD6 has positive staining in mature T cells, B1 cells, NK cells, CNS cells (basalganglia and cortex cerebellum), and mature medullary thymocytes.
References: Nat Genet. 2009 Jul;41(7):776-82, PMID: 19525953, J Immunol. 2011 Sep 15;187(6):3286-91, PMID: 21849685; J Innate Immun 2011;3:420, PMID: 21178331; Journal of Neuroimmunology. 1990 Oct. 29(1–3):193-202, DOI: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90162-G; Journal of Crohn's and Colitis. 2019 Apr. 13(4):510–524, DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy179
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
CD6
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(3)
Flo
(3)
Func
(1)
IP
(1)
Host
mouse
(3)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(3)
Isotype
IgG1
(1)
IgG1,k
(2)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(3)
Clone
MEM-98
(1)
UMCD6/3F7B5
(1)
Format
Azide-free
(1)
Unconjugated
(3)
Publications
No
(3)

Cancer
CD6 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Azide-free) (UMCD6/3F7B5) Antibody
Human
Flo, Func, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated, Azide-free
100 µg/$375

Cancer
CD6 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (MEM-98) Antibody
Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

Cancer
CD6 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal Antibody
Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µg/$495
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











