Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CD14 Antibodies
CD14, also called monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, is a co-receptor protein for bacterial lipopolysaccharide. It is a component of the innate immune system, enhancing responses to infection by sensitizing host cells to bacterial lipopolysaccharide and other microbial products. Binding to LPS activates the release of cytokines. CD14 has a membrane-bound form and a soluble form. It is expressed on macrophages, monocytes (specific marker for monocytic differentiation), neutrophils, dendritic cells, and enterocytes; the soluble form is secreted by the liver and by monocytes. Staining is used to identify monocytes and macrophages in normal tissues and leukemias (eg, acute monoblastic, acute myelomonocytic).
References: Science. 1990;249(4975):1431-1433. PMID: 1698311; Immunity. 1994;1(6):509-516. PMID: 7534618; J Hepatol. 1999;31(3):435-442. PMID: 10488701; Infect Immun. 1998;66(3):1135-1141. PMID: 9488406; Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135(5):720-730. doi: 10.1309/AJCPZ46PMMAWJROT; -Leukemia. 2006;20(7):1321-1324. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404242
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
CD14
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(2)
Host
mouse
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(2)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG2a
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(2)
Clone
7
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
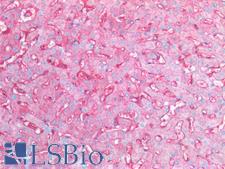
CD14 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (7) Antibody
Human
IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.05 ml/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
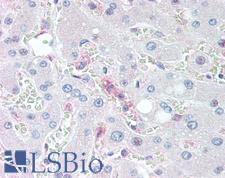
CD14 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











