Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
| Catalog Number | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|
| LS-B9984-50 | 50 µg (1 mg/ml) | $375 |
IHC‑plus™ Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human GAD65 Antibody (clone N‑GAD65, aa4‑22, IHC, WB) LS‑B9984
IHC‑plus™ Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human GAD65 Antibody (clone N‑GAD65, aa4‑22, IHC, WB) LS‑B9984
Note: This antibody replaces LS-C188636
Antibody:
GAD65 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (aa4-22) (N-GAD65) Antibody
Application:
IHC, IHC-P, WB, IP, RIA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Toll Free North America
 (800) 227-6666
(800) 227-6666
For Research Use Only
Overview
Antibody:
GAD65 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (aa4-22) (N-GAD65) Antibody
Application:
IHC, IHC-P, WB, IP, RIA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Specifications
Description
GAD65 antibody LS-B9984 is an unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody to human GAD65 (aa4-22). Validated for IHC, IP, RIA and WB. Tested on 20 paraffin-embedded human tissues.
Target
Human GAD65
Synonyms
GAD2 | GAD-65 | Glutamate decarboxylase 2 | GAD65
Host
Mouse
Reactivity
Human
(tested or 100% immunogen sequence identity)
Clonality
IgG1
Monoclonal
Clone
N-GAD65
Conjugations
Unconjugated
Purification
Protein G purified
Modifications
Unmodified
Immunogen
Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) conjugated synthetic peptide sequence PGSGFWSFGSEDGSGDSEN corresponding to amino acids 4-22 within the N-Terminus of human GAD65. Percent identity by BLAST analysis: Human, Chimpanzee, Gorilla, Orangutan (100%); Gibbon, Galago, Rat, Ferret, Panda, Bovine, Cat, Dog, Horse, Pig (95%); Monkey, Marmoset, Mouse, Rabbit, Opossum, Guinea pig (89%).
Epitope
aa4-22
Specificity
Recognizes an epitope within the N-terminal (NT) region of Glutamate decarboxylase 2, otherwise known as GAD65/GAD2, an amphiphilic membrane-anchored protein and member of the group 2 decarboxylase family, principally expressed in the brain and also in pancreatic beta cells. GAD65 catalyzes the decarboxylation of glutamate to GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. GAD65 is the 65kD isoform of GAD, encoded by the GAD2 gene, which is predominantly expressed by nerve termini, as oppose to the 67kD isoform (GAD67), which is predominantly found in the cell body, and is encoded by the GAD1 gene. Studies have shown the presence of autoantibodies to GAD65 (GAD65Ab) in autoimmune diseases, including Graves disease and Stiff Man Syndrome (SMS), but GAD65Ab are most prevalent in patients with Type I diabetes mellitus, and those at high risk of developing Type I diabetes. The N-Terminal region of GAD65 lacks the epitopes for GAD65Ab in Type I diabetes patients, and has been shown as essential for targeting the enzyme to GABA-containing secretory vesicles. Clone N-GAD65 has been shown to be highly specific for GAD65 and does not recognize GAD67.
Applications
- IHC
- IHC - Paraffin (5 µg/ml)
- Western blot (1:100 - 1:1000)
- Immunoprecipitation
- Radioimmunoassay
|
Performing IHC? See our complete line of Immunohistochemistry Reagents including antigen retrieval solutions, blocking agents
ABC Detection Kits and polymers, biotinylated secondary antibodies, substrates and more.
|
Presentation
PBS, 0.09% Sodium Azide
Storage
Store at 4°C or at -20°C. Store undiluted. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Microcentrifugation recommended if solution contains precipitate.
Restrictions
For research use only. Intended for use by laboratory professionals.
About GAD65
Validation
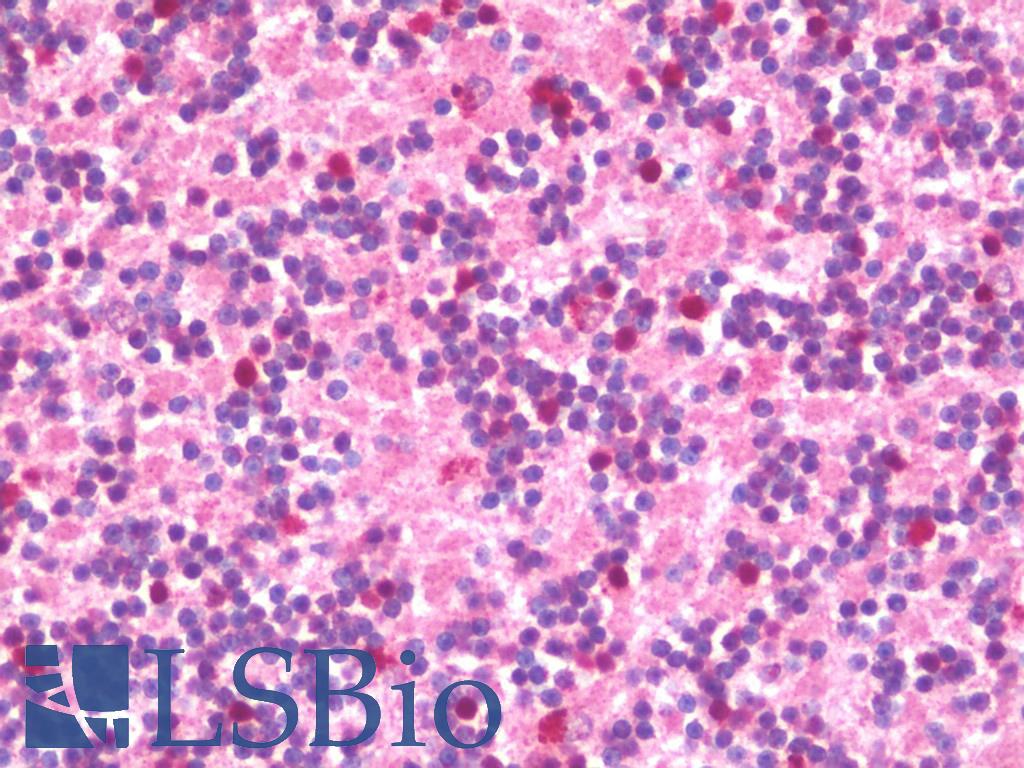
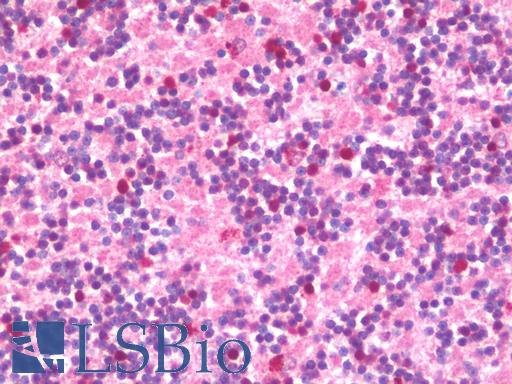
Anti-GAD65 antibody IHC staining of human brain, cerebellum. Immunohistochemistry of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue after heat-induced antigen retrieval. Antibody concentration 5 ug/ml.
Anti-GAD65 antibody IHC staining of human brain, cerebellum. Immunohistochemistry of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue after heat-induced antigen retrieval. Antibody concentration 5 ug/ml.
See More About...
LSBio Ratings
IHC-plus™ GAD65 Antibody (aa4-22, clone N-GAD65) for IHC, WB/Western, IP LS-B9984 has an LSBio Rating of
Laboratory Validation Score (4)
Learn more about The LSBio Ratings Algorithm
Publications (0)
Customer Reviews (0)
Featured Products
Species:
Human, Monkey, Mouse
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Western blot, Peptide Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Western blot
Species:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications:
ICC, Immunofluorescence, Western blot
Species:
Human
Applications:
IHC, Immunofluorescence, Western blot, ELISA
Request SDS/MSDS
To request an SDS/MSDS form for this product, please contact our Technical Support department at:
Technical.Support@LSBio.com
Requested From: United States
Date Requested: 4/2/2025
Date Requested: 4/2/2025


![GAD65 Antibody - GAD65 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects GAD2 protein at cytosol on RT2 xenograft by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded RT2 xenograft. GAD65 antibody [C2C3], C-term dilution:1:500.](https://lsbio-7d62.kxcdn.com//image2/gad65-antibody-aa465-558-ls-c185356/137482_723191.jpg)