order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
TGF-Beta
TGFB / TGF Beta / Transforming Growth Factor Beta
Transforming growth factor beta is a secreted protein that controls proliferation, cellular differentiation, and other functions in most cells. It is a type of cytokine which plays a role in immunity, cancer, bronchial asthma, lung fibrosis, heart disease, diabetes, Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, Marfan syndrome, Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Loeys–Dietz syndrome, Parkinson's disease, Chronic kidney disease, Multiple Sclerosis and AIDS. TGF-beta is secreted by many cell types, including macrophages, in a latent form in which it is complexed with two other polypeptides, latent TGF-beta binding protein (LTBP) and latency-associated peptide (LAP). Serum proteinases such as plasmin catalyze the release of active TGF-beta from the complex. This often occurs on the surface of macrophages where the latent TGF-beta complex is bound to CD36 via its ligand, thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1). Inflammatory stimuli that activate macrophages enhance the release of active TGF-ß by promoting the activation of plasmin. Macrophages can also endocytose IgG-bound latent TGF-ß complexes that are secreted by plasma cells and then release active TGF-beta into the extracellular fluid. It exists in at least three isoforms called TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3. Until the three isoforms were discovered, TGF-beta referred to TGF-beta1, as it was the first member of this family to be discovered.
TGF-Beta Target Details
| Target Name: | TGFB / TGF Beta / Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
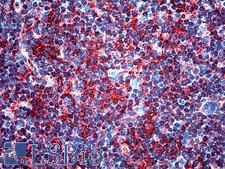
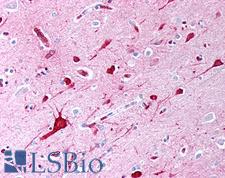



If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.











