order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
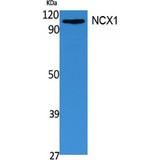
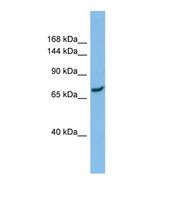
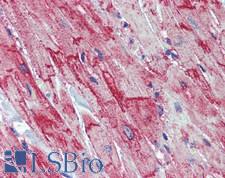
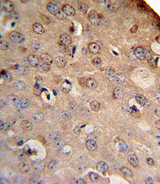
SLC8A1 / NCX1
solute carrier family 8 (sodium/calcium exchanger), member 1
In cardiac myocytes, Ca(2+) concentrations alternate between high levels during contraction and low levels during relaxation. The increase in Ca(2+) concentration during contraction is primarily due to release of Ca(2+) from intracellular stores. However, some Ca(2+) also enters the cell through the sarcolemma (plasma membrane). During relaxation, Ca(2+) is sequestered within the intracellular stores. To prevent overloading of intracellular stores, the Ca(2+) that entered across the sarcolemma must be extruded from the cell. The Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger is the primary mechanism by which the Ca(2+) is extruded from the cell during relaxation. In the heart, the exchanger may play a key role in digitalis action. The exchanger is the dominant mechanism in returning the cardiac myocyte to its resting state following excitation.
| Gene Name: | solute carrier family 8 (sodium/calcium exchanger), member 1 |
| Family/Subfamily: | Transporter , Calcium:cation antiporter |
| Synonyms: | SLC8A1, CNC, NCX1, Sodium calcium exchanger 1, Sodium/calcium exchanger 1, Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, Na+/Ca++ exchanger |
| Target Sequences: | NM_021097 NP_066920.1 P32418 |
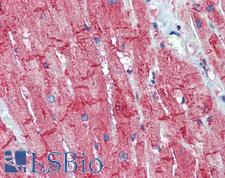
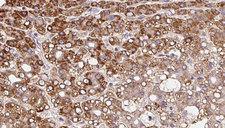
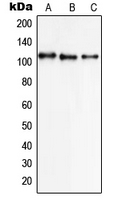

If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.











