order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
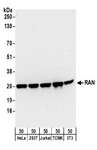
RAN
RAN, member RAS oncogene family
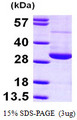
RAN (ras-related nuclear protein) is a small GTP binding protein belonging to the RAS superfamily that is essential for the translocation of RNA and proteins through the nuclear pore complex. The RAN protein is also involved in control of DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression. Nuclear localization of RAN requires the presence of regulator of chromosome condensation 1 (RCC1). Mutations in RAN disrupt DNA synthesis. Because of its many functions, it is likely that RAN interacts with several other proteins. RAN regulates formation and organization of the microtubule network independently of its role in the nucleus-cytosol exchange of macromolecules. RAN could be a key signaling molecule regulating microtubule polymerization during mitosis. RCC1 generates a high local concentration of RAN-GTP around chromatin which, in turn, induces the local nucleation of microtubules. RAN is an androgen receptor (AR) coactivator that binds differentially with different lengths of polyglutamine within the androgen receptor. Polyglutamine repeat expansion in the AR is linked to Kennedy's disease (X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy). RAN coactivation of the AR diminishes with polyglutamine expansion within the AR, and this weak coactivation may lead to partial androgen insensitivity during the development of Kennedy's disease.
| Gene Name: | RAN, member RAS oncogene family |
| Family/Subfamily: | Ras GTPase superfamily IPR001806 , RAS oncogene |
| Synonyms: | RAN, Gsp1, Guanosine triphosphatase Ran, RanGTPase, Member RAS oncogene family, OK/SW-cl.81, Ras-related nuclear protein, ARA24, TC4, GTPase Ran, Ras-like protein TC4 |
| Target Sequences: | NM_006325 NP_006316.1 P62826 |
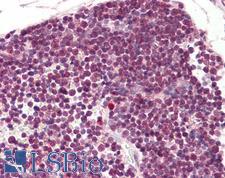
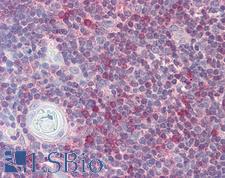
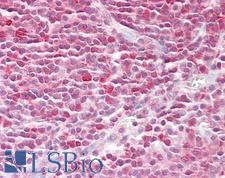
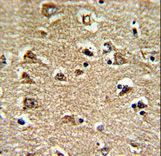
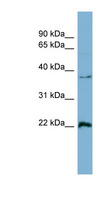
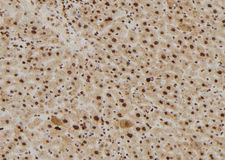
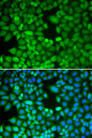

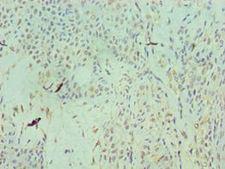


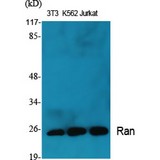
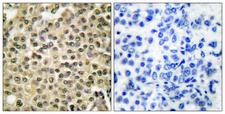
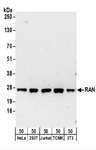
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.