order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
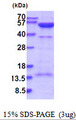
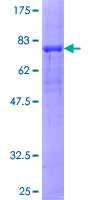
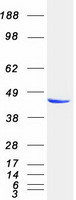
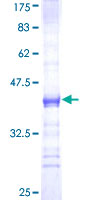
PRKAR2A
protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type II, alpha
cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive kinase holoenzyme is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the regulatory subunits. This subunit can be phosphorylated by the activated catalytic subunit. It may interact with various A-kinase anchoring proteins and determine the subcellular localization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. This subunit has been shown to regulate protein transport from endosomes to the Golgi apparatus and further to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
| Gene Name: | protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type II, alpha |
| Family/Subfamily: | Protein Kinase Non Catalytic , not assigned-Protein Kinase Non Catalytic |
| Synonyms: | PRKAR2A, PKR2, PRKAR2 |
| Target Sequences: | BT007225 AAP35889.1 P13861 |
Publications (1)
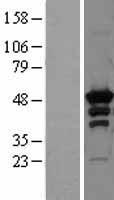
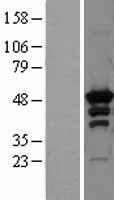
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.