order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
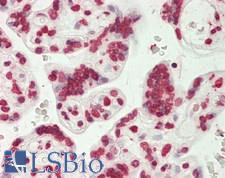
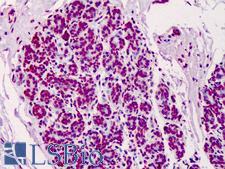
PAR / Poly ADP-Ribose
Poly (ADP-ribose) is synthesized by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARP), which catalyzes the formation of the polymer PADPR, with chain lengths ranging from 2 to 300 residues. PARP is found in the cell’s nucleus. The main role is to detect and signal single-strand DNA breaks (SSB) to the enzymatic machinery involved in the SSB repair. PARP activation is an immediate cellular response to metabolic, chemical, or radiation-induced DNA SSB damage. Once PARP detects a SSB, it binds to the DNA, and, after a structural change, begins the synthesis of a poly (ADP-ribose) chain (PAR) as a signal for the other DNA-repairing enzymes such as DNA ligase III (LigIII), DNA polymerase beta (polß), and scaffolding proteins such as X-ray cross-complementing gene 1 (XRCC1). After repairing, the PAR chains are degraded via Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG).
PAR / Poly ADP-Ribose Target Details
| Target Name: | PAR / Poly ADP-Ribose |
Publications (1)
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.










