order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
KCNMA1 / BK
potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, alpha member 1
Potassium channel activated by both membrane depolarization or increase in cytosolic Ca2+ that mediates export of K+. It is also activated by the concentration of cytosolic Mg2+. Its activation dampens the excitatory events that elevate the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and/or depolarize the cell membrane. It therefore contributes to repolarization of the membrane potential. Plays a key role in controlling excitability in a number of systems, such as regulation of the contraction of smooth muscle, the tuning of hair cells in the cochlea, regulation of transmitter release, and innate immunity. In smooth muscles, its activation by high level of Ca2+, caused by ryanodine receptors in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, regulates the membrane potential. In cochlea cells, its number and kinetic properties partly determine the characteristic frequency of each hair cell and thereby helps to establish a tonotopic map. Kinetics of KCNMA1 channels are determined by alternative splicing, phosphorylation status and its combination with modulating beta subunits. Highly sensitive to both iberiotoxin (IbTx) and charybdotoxin (CTX).
| Gene Name: | potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, alpha member 1 |
| Family/Subfamily: | Ion Channel , Potassium channel - calcium-activated |
| Synonyms: | KCNMA1, BA205K10.1, BKCA alpha subunit, BK channel, BKCA alpha, BKTM, HSlo, K(VCA)alpha, KCa1.1, Maxi-K channel HSLO, MaxiK, KCNMA, SAKCA, SLO-ALPHA, Slowpoke homolog, Stretch-activated Kca channel, Slo homolog, BK channel alpha subunit, Maxi K channel, MSlo, MSLO1, SLO, SLO1 |
| Target Sequences: | NM_002247 NP_002238.2 Q12791 |
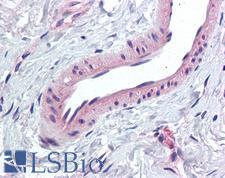
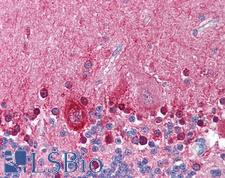
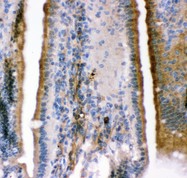
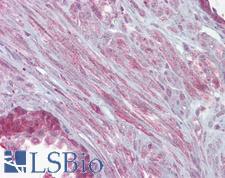
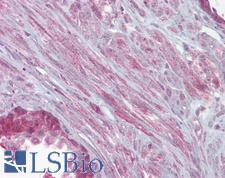
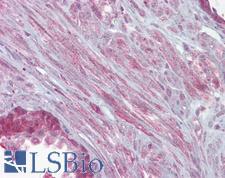
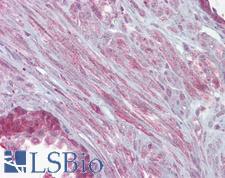
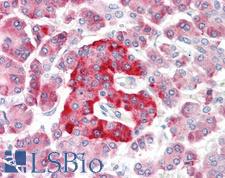
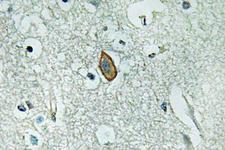

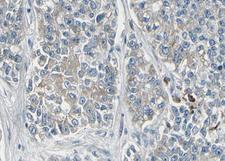
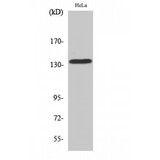
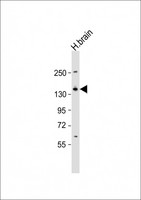
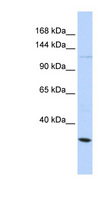
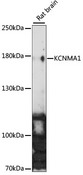
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.










