order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Human IgG
Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in the circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. IgG antibodies are large molecules of about 150 kDa made of four peptide chains. It contains two identical class gamma heavy chains of about 50 kDa and two identical light chains of about 25 kDa. The two heavy chains are linked to each other and to a light chain each by disulfide bonds. The resulting tetramer has two identical halves, which together form the Y-like shape. Each end of the fork contains an identical antigen binding site. The Fc regions of IgGs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. There are four IgG subclasses (IgG1, 2, 3, and 4) in humans, named in order of their abundance in serum (IgG1 being the most abundant).
Human IgG Target Details
| Target Name: | Human IgG |
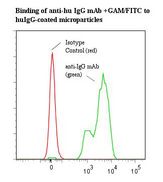
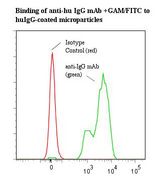
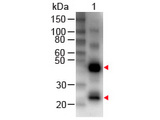
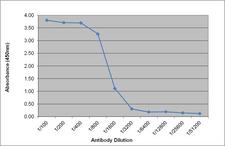

If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.









