order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
HAS2
hyaluronan synthase 2
Hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid (HA) is a high molecular weight unbranched polysaccharide synthesized by a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals, and is a constituent of the extracellular matrix. It consists of alternating glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine residues that are linked by beta-1-3 and beta-1-4 glycosidic bonds. HA is synthesized by membrane-bound synthase at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, and the chains are extruded through pore-like structures into the extracellular space. It serves a variety of functions, including space filling, lubrication of joints, and provision of a matrix through which cells can migrate. HA is actively produced during wound healing and tissue repair to provide a framework for ingrowth of blood vessels and fibroblasts. Changes in the serum concentration of HA are associated with inflammatory and degenerative arthropathies such as rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, the interaction of HA with the leukocyte receptor CD44 is important in tissue-specific homing by leukocytes, and overexpression of HA receptors has been correlated with tumor metastasis. HAS2 is a member of the newly identified vertebrate gene family encoding putative hyaluronan synthases, and its amino acid sequence shows significant homology to glycosaminoglycan synthetase (DG42) from Xenopus laevis, and human and murine hyaluronan synthase 1.
| Gene Name: | hyaluronan synthase 2 |
| Synonyms: | HAS2, Hyaluronic acid synthase 2, HA synthase 2, Hyaluronan synthase 2, Hyaluronate synthase 2 |
| Target Sequences: | NM_005328 NP_005319.1 Q92819 |
Publications (3)
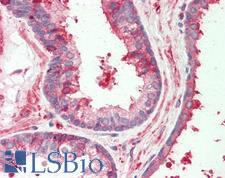
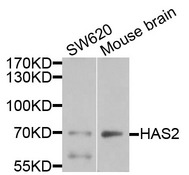
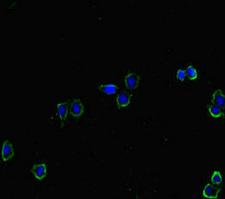
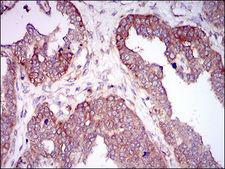
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.










