order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
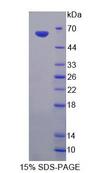
Endonuclease G / ENDOG
endonuclease G
The fragmentation of nuclear DNA is a hallmark of apoptotic cell death. The activities of caspase and nuclease are involved in the DNA fragmentation. Caspase-activated deoxyribonuclease (CAD), also termed DNA fragmentation factor (DFF40), is one such nuclease, and is capable of inducing DNA fragmentation and chromatin condensation after cleavage by caspase-3 of its inhibitor ICAD/DFF45. Caspase and CAD independent DNA fragmentation also exists. Recent studies demonstrated that another nuclease, endonuclease G (endoG), is specifically activated by apoptotic stimuli and is able to induce nucleosomal fragmentation of DNA independently of caspase and DFF/CAD. EndoG is a mitochondrion-specific nuclease that translocates to the nucleus and cleaves chromatin DNA during apoptosis. The homologue of mammalian EndoG is the first mitochondrial protein identified to be involved in apoptosis in C. elegans. EndooG also cleaves DNA in vitro.
| Gene Name: | endonuclease G |
| Family/Subfamily: | Endonuclease , Not assigned-Endonuclease |
| Synonyms: | ENDOG, Endonuclease G, mitochondrial, Mitochondrial endonuclease G, Endo G, Endonuclease G |
| Target Sequences: | NM_004435 NP_004426.2 Q14249 |
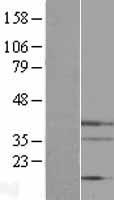
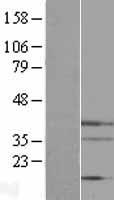
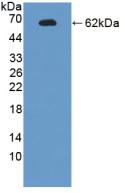
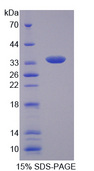

If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.









