order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
COX6A1
cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIa polypeptide 1
Cytochrome c oxidase (COX), the terminal enzyme of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, catalyzes the electron transfer from reduced cytochrome c to oxygen. It is a heteromeric complex consisting of 3 catalytic subunits encoded by mitochondrial genes and multiple structural subunits encoded by nuclear genes. The mitochondrially-encoded subunits function in the electron transfer and the nuclear-encoded subunits may function in the regulation and assembly of the complex. This nuclear gene encodes polypeptide 1 (liver isoform) of subunit VIa, and polypeptide 1 is found in all non-muscle tissues. Polypeptide 2 (heart/muscle isoform) of subunit VIa is encoded by a different gene, and is present only in striated muscles. These two polypeptides share 66% amino acid sequence identity. It has been reported that there may be several pseudogenes on chromosomes 1, 6, 7q21, 7q31-32 and 12. However, only one pseudogene (COX6A1P) on chromosome 1p31.1 has been documented.
| Gene Name: | cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIa polypeptide 1 |
| Synonyms: | COX6A1, COX6A, COX6AL, COX VIa-L |
| Target Sequences: | NM_004373 NP_004364.2 P12074 |
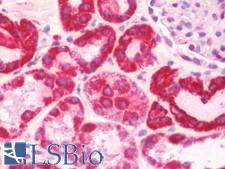
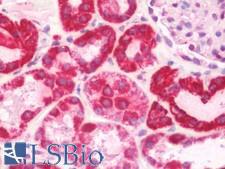
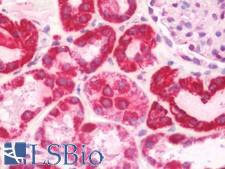
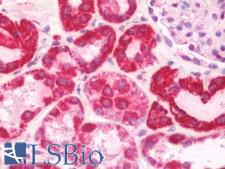
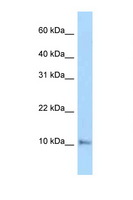
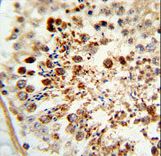
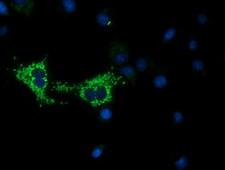
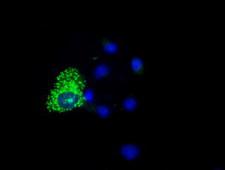
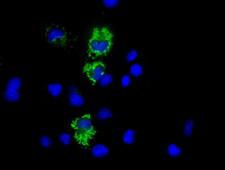
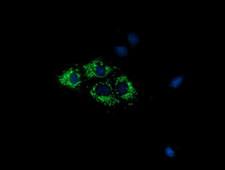
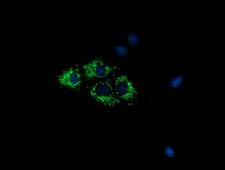
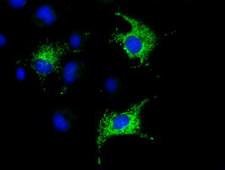
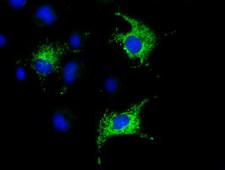
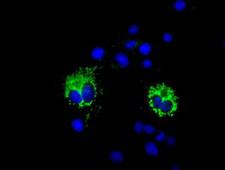
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.











