order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
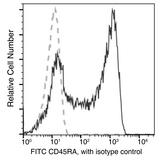
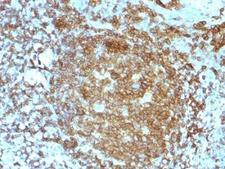
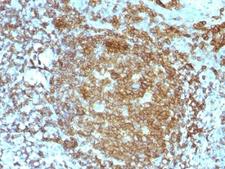
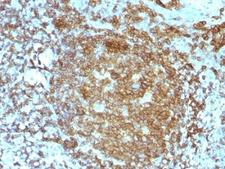
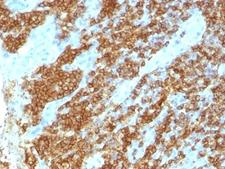
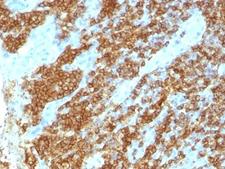
CD45RA
Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, C also known as PTPRC is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the PTPRC gene. PTPRC is also known as CD45 antigen (CD stands for cluster of differentiation), which was originally called leukocyte common antigen (LCA). The CD45 family consists of multiple members that are all products of a single complex gene. This gene contains 34 exons and three exons of the primary transcripts are alternatively spliced to generate up to eight different mature mRNAs and after translation eight different protein products. These three exons generate the RA, RB and RC isoforms. Various isoforms of CD45 exist: CD45RA, CD45RB, CD45RC, CD45RAB, CD45RAC, CD45RBC, CD45RO, CD45R (ABC). CD45RA is located on naive T cells and CD45RO is located on memory T cells. CD45 is also highly glycosylated. CD45R is the longest protein and migrates at 200 kDa when isolated from T cells. B cells also express CD45R with heavier glycosylation, bringing the molecular weight to 220 kDa, hence the name B220; B cell isoform of 220 kDa. B220 expression is not restricted to B cells and can also be expressed on activated T cells, on a subset of dendritic cells and other antigen-presenting cells. Naive T lymphocytes express large CD45 isoforms and are usually positive for CD45RA. Activated and memory T lymphocytes express the shortest CD45 isoform, CD45RO, which lacks RA, RB, and RC exons. This shortest isoform facilitates T cell activation. The cytoplasmic domain of CD45 is one of the largest known and it has an intrinsic phosphatase activity that removes an inhibitory phosphate group on a tyrosine kinase called Lck (in T cells) or Lyn/Fyn/Lck (in B cells) and activates it.
CD45RA Target Details
| Target Name: | CD45RA |
Publications (8)
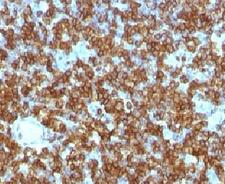
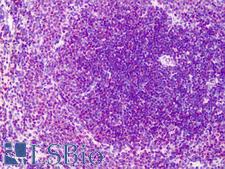
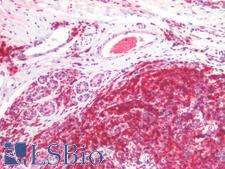
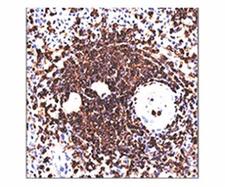
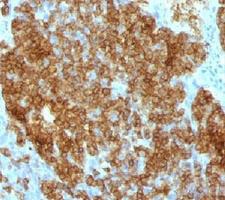
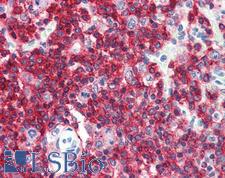
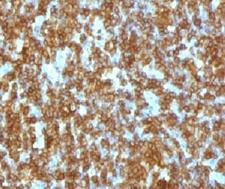
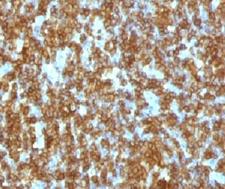
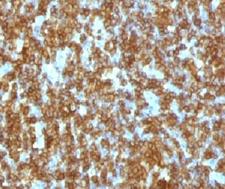
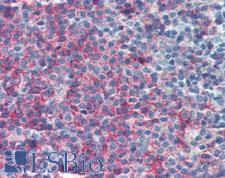
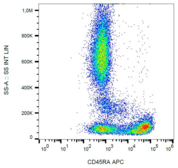
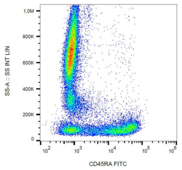
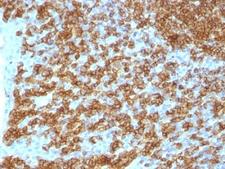
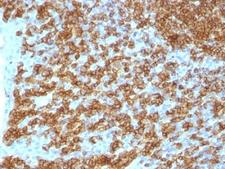
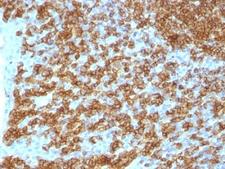
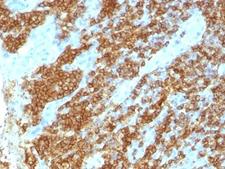
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.










