order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
BUB1
BUB1 mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine kinase
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that performs 2 crucial functions during mitosis: it is essential for spindle-assembly checkpoint signaling and for correct chromosome alignment. Has a key role in the assembly of checkpoint proteins at the kinetochore, being required for the subsequent localization of CENPF, BUB1B, CENPE and MAD2L1. Required for the kinetochore localization of PLK1. Plays an important role in defining SGOL1 localization and thereby affects sister chromatid cohesion. Acts as a substrate for anaphase-promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C) in complex with its activator CDH1 (APC/C-Cdh1). Necessary for ensuring proper chromosome segregation and binding to BUB3 is essential for this function. Can regulate chromosome segregation in a kinetochore-independent manner. Can phosphorylate BUB3. The BUB1-BUB3 complex plays a role in the inhibition of APC/C when spindle-assembly checkpoint is activated and inhibits the ubiquitin ligase activity of APC/C by phosphorylating its activator CDC20. This complex can also phosphorylate MAD1L1. Kinase activity is essential for inhibition of APC/CCDC20 and for chromosome alignment but does not play a major role in the spindle-assembly checkpoint activity. Mediates cell death in response to chromosome missegregation and acts to suppress spontaneous tumorigenesis.
| Gene Name: | BUB1 mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine kinase |
| Family/Subfamily: | Protein Kinase , BUB1 |
| Synonyms: | BUB1, Bub1A, BUB1L, HBUB1 |
| Target Sequences: | NM_004336 NP_004327.1 O43683 |
Publications (1)
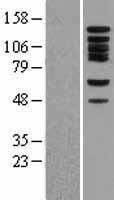

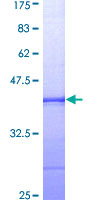
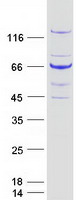
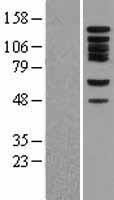
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.









