order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
ATP6V1G2
ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G2
ATP6V1G2 is a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of intracellular compartments of eukaryotic cells. V-ATPase dependent acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c', and d. Additional isoforms of many of the V1 and V0 subunit proteins are encoded by multiple genes or alternatively spliced transcript variants. This encoded protein is one of three V1 domain G subunit proteins. This gene had previous gene symbols of ATP6G and ATP6G2. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the downstream DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 39B (DDX39B) gene.
| Gene Name: | ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G2 |
| Family/Subfamily: | Transporter , ATPase - V type |
| Synonyms: | ATP6V1G2, ATP6G, ATP6G2, Em:AC004181.3, NG38, Vma10, V-ATPase 13 kDa subunit 2, V-ATPase subunit G 2 |
| Target Sequences: | NM_138282 NP_612139.1 O95670 |
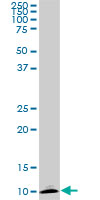
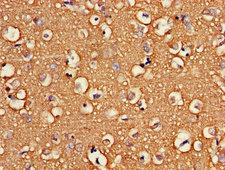






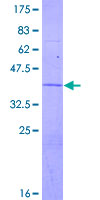

If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.










