order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
ATP6V0E2
ATPase, H+ transporting V0 subunit e2
Multisubunit vacuolar-type proton pumps, or H(+)-ATPases, acidify various intracellular compartments, such as vacuoles, clathrin-coated and synaptic vesicles, endosomes, lysosomes, and chromaffin granules. H(+)-ATPases are also found in plasma membranes of specialized cells, where they play roles in urinary acidification, bone resorption, and sperm maturation. Multiple subunits form H(+)-ATPases, with proteins of the V1 class hydrolyzing ATP for energy to transport H+, and proteins of the V0 class forming an integral membrane domain through which H+ is transported. ATP6V0E2 encodes an isoform of the H(+)-ATPase V0 e subunit, an essential proton pump component (Blake-Palmer et al., 2007 [PubMed 17350184]).
| Gene Name: | ATPase, H+ transporting V0 subunit e2 |
| Synonyms: | ATP6V0E2, ATP6V0E2L, C7orf32, H+-ATPase e2 subunit, Vacuolar proton-ATPase subunit, V-ATPase subunit E 2 |
| Target Sequences: | NP_001094062.1 Q8NHE4 |
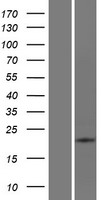
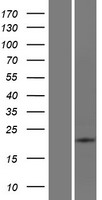
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.










