order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
AR / Androgen Receptor
androgen receptor
The androgen receptor (AR) is a NR3 Steroid Receptor located on the X chromosome. AR is a phosphoprotein and acts as a steroid hormone-activated transcription factor for androgen-responsive genes. Mutations in the AR gene are associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome (CAIS) or testicular feminization syndrome, Reifenstein syndrome, and Kennedy spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. They lead to symptoms such as low virilization, reduced sperm production, testicular atrophy, and infertility. Androgen signaling through the androgen receptor (AR) appears to be involved in all aspects of prostate cancer, from initiation to development of treatment resistance. Gain-of-function AR gene mutations and/or altered signaling through AR have been suggested to contribute to disease progression. A recent study showed decreased expression of AR in response to incubation of LNCaP prostate carcinoma cells with PC-SPES, a mixture of eight herbs (Bonham et al. 2002). Two forms of AR that differ in their N termini have been isolated: AR A (87 kD), which is derived from translation of an internal methionine codon (met188), and AR B (110 kD). The two isoforms are expressed in similar tissues; however, AR B generally is the more abundant form.
| Gene Name: | androgen receptor |
| Family/Subfamily: | NHR , NR3 Steroid receptor |
| Synonyms: | AR, Androgen receptor, Dihydrotestosterone receptor, DHTR, AIS, KD, NR3C4, HUMARA, SBMA, TFM, SMAX1, HYSP1 |
| Target Sequences: | NM_000044 NP_000035.2 P10275 |
Publications (4)
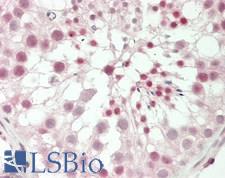
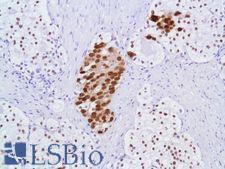
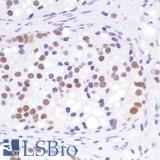
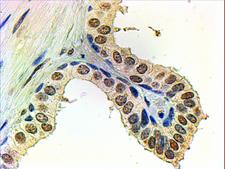
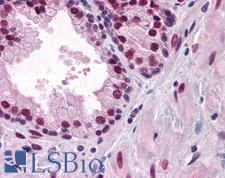
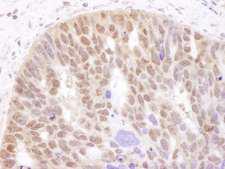



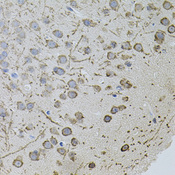
![AR / Androgen Receptor Antibody - Immunoperoxidase of monoclonal antibody to AR on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human renal cell carcinoma tissue. [antibody concentration 3 ug/ml].](https://lsbio-7d62.kxcdn.com/image2/ar-androgen-receptor-antibody-clone-1g3-ls-c133049/50204_4834017.jpg)
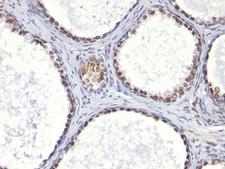


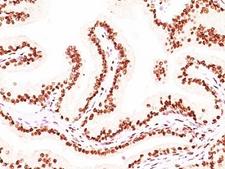
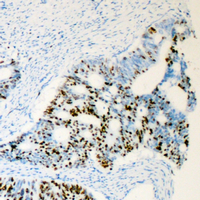
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.











