order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
ACE2 / ACE-2
angiotensin I converting enzyme 2
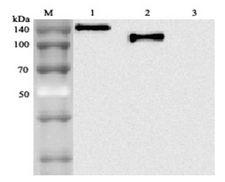
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) plays a central role in vascular, renal, and myocardial physiology. In contrast to its homolog ACE, ACE2 expression is restricted to heart, kidney, and testis. The normal function of ACE2 is to convert the inactive vasoconstrictor angiotensin I (AngI) to Ang1-9 and the active form AngII to Ang1-7, unlike ACE, which converts AngI to AngII. While the role of these vasoactive peptides is not well understood, lack of ACE2 expression in ace2-/ace2- mice leads to severely reduced cardiac contractility, indicating its importance in regulating heart function. ACE2 is also the attachment receptor for HCoV-N63, SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. The S1 portion of the coronavirus spike protein attaches to ACE2 presented on the host cell surface. The SARS-CoV-2 virus targets pneumocytes and macrophages expressing ACE2 in the lung, and it is believed to infect ACE2-positive cells in other tissues including the gastrointestinal tract and potentially the liver (in cholangiocytes).
| Gene Name: | angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 |
| Family/Subfamily: | Protease , Metallopeptidase M2 |
| Synonyms: | ACE2, ACE-related carboxypeptidase, ACEH, Metalloprotease MPROT15, SARS-CoV2 Coronavirus Receptor, SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Receptor, COVID-19 viral receptor |
| Target Sequences: | NM_021804 NP_068576.1 Q9BYF1 |
Publications (10)
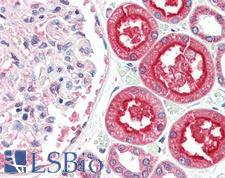
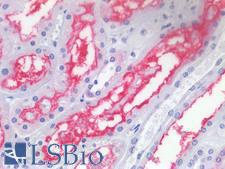
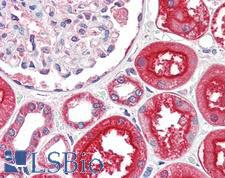
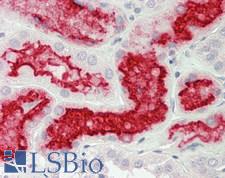
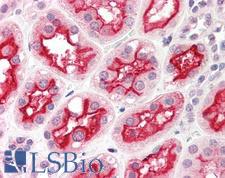

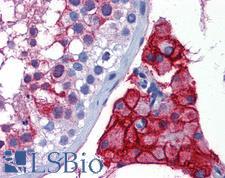
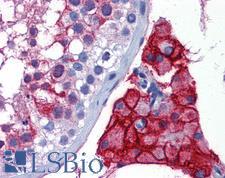
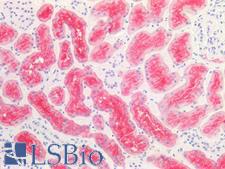





If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.













