order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
ABCG8
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 8
ABCG8 is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the White subfamily. The protein encoded by this gene functions to exclude non-cholesterol sterol entry at the intestinal level, promote excretion of cholesterol and sterols into bile, and to facilitate transport of sterols back into the intestinal lumen. It is expressed in a tissue-specific manner in the liver, intestine, and gallbladder. This gene is tandemly arrayed on chromosome 2, in a head-to-head orientation with family member ABCG5. Mutations in this gene may contribute to sterol accumulation and atherosclerosis, and have been observed in patients with sitosterolemia.
| Gene Name: | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G (WHITE), member 8 |
| Family/Subfamily: | Transporter , ATP-binding cassette - ABCG/WHITE |
| Synonyms: | ABCG8, Sterolin-2, STSL, GBD4, Sterolin 2 |
| Target Sequences: | NM_022437 NP_071882.1 Q9H221 |
Publications (3)
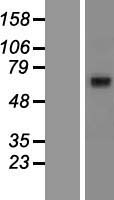
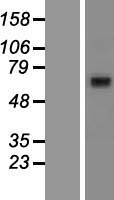
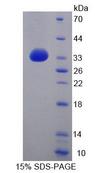
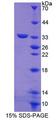
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.










