Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM SYNCAM / CADM1 Antibodies
CADM1 (Cell adhesion molecule 1, BL2, IGSF4) is a membrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is involved in cell-cell interaction, epithelial and synaptic adhesion, neural development and tumor suppression. In the brain, it is expressed on Purkinje cell dendrites in the cerebellum and on neural dendrites in the hippocampus. Inherited mutations in CADM1 are correlated with autism. Furthermore, knockout studies in mice indicate that loss of CADM1 results in arrested spermatogenesis and infertility. CADM1 has also been found to function in the suppression of tumor motility and invasive characteristics. In breast cancer, loss of CADM1 is an indicator of poor prognosis and metastasis to the brain. Similarly, higher expression of CADM1 in melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the lung is associated with better survival. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, CADM1 has high membranous positivity in the central nervous system, and is also expressed on most glandular cells, basolateral renal tubule membranes, and islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.
References: Oncotarget. 2014 May 30;5(10):3076-87, PMID: 24833255; J. Neurochem.2012. 2012 (123): 886–894, DOI: 10.1111/jnc.12022; Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018; 6: 86, PMID: 30131958; Cell Death & Diseasevolume 10, Article number: 281 (2019); Cell Death Dis. 2019 Mar 25;10(4):281, PMID: 30911007; Scientific Reports. Volume 6, Article number: 24006 (2016);
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
SYNCAM / CADM1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
aa393-442
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
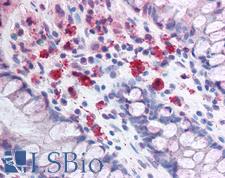
SYNCAM / CADM1 Rabbit anti-Rat Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.1 ml/$460

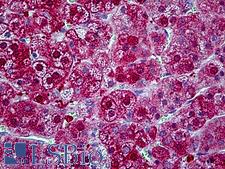
Neuroscience
SYNCAM / CADM1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa393-442) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










