Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM STK11 / LKB1 Antibodies
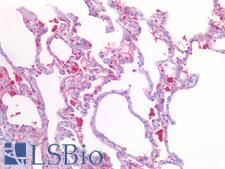
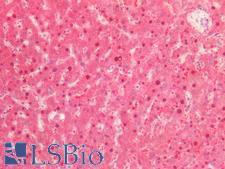
STK11 is a serine/threonine-protein kinase that controls the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) family members and also functions as a tumor suppressor. It functions in cell metabolism, cell polarity, apoptosis and DNA damage response. It is a key upstream regulator of AMPK, mediating the phosphorylation and activation of AMPK catalytic subunits PRKAA1 and PRKAA2. It thereby regulates the inhibition of signaling pathways that promote cell growth and proliferation when energy levels are low, glucose homeostasis in liver, activation of autophagy when cells undergo nutrient deprivation, and B-cell differentiation in the germinal center in response to DNA damage. It also modulates cellular polarity by remodeling the actin cytoskeleton. STK11 is required for cortical neuron polarization by mediating phosphorylation and activation of BRSK1 and BRSK2, leading to axon initiation and specification. It is also involved in DNA damage response via p53/TP53 and is recruited to the CDKN1A/WAF1 promoter to participate in transcription activation. In vein endothelial cells, STK11 inhibits PI3K/Akt signaling activity and thus induces apoptosis in response to the oxidant peroxynitrite in vitro. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, STK11 has moderate cytoplasmic positivity in all tissues throughout the body.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804;
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
STK11 / LKB1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(2)
Monkey
(1)
Application
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
IF
(1)
IP
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(2)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(1)
Clone
27D10
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Cancer
STK11 / LKB1 Rabbit anti-Human Monoclonal (27D10) Antibody
Rat, Human, Monkey
IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$565

Cancer
STK11 / LKB1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IF, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










