Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM SSTR3 Antibodies
SSTR3 is a member of the somatostatin receptor protein family. Somatostatins are peptide hormones that regulate diverse cellular functions such as neurotransmission, cell proliferation, and endocrine signaling as well as inhibiting the release of many hormones and other secretory proteins. Somatostatin has two active forms of 14 and 28 amino acids. The biological effects of somatostatins are mediated by a family of G-protein coupled somatostatin receptors that are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. Somatostatin receptors form homodimers and heterodimers with other members of the superfamily as well as with other G-protein coupled receptors and receptor tyrosine kinases. This protein is functionally coupled to adenylyl cyclase. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
SSTR3
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
GPCR Database Antibodies
(1)
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Publications
Yes
(1)

Cancer
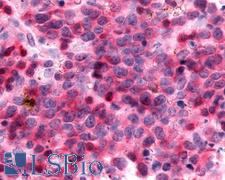
SSTR3 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results










