Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
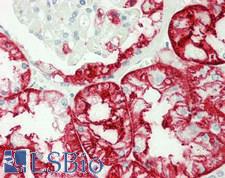
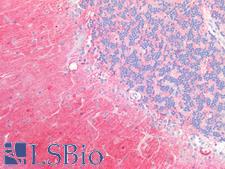
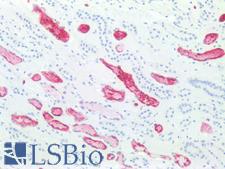
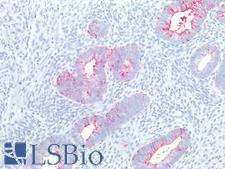
PathPlusTM SSEA-1 / Lewis x / CD15 Antibodies
SSEA-1 (CD15, Lewis x) is a cell-surface carbohydrate antigen synthesized by FUT4 and FUT9. This carbohydrate plays a role in cell-to-cell recognition and also functions to inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis, activate normal monocytes, and mediate phagocytosis. SSEA-1 is expressed on the majority of granulocytes, up to 60% of monocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils, in proximal and distal renal tubules, and activated B and T cells. It is not present on lymphocytes. It is a useful marker for classic and follicular Hodgkin lymphoma, as it shows membranous and cytoplasmic staining in Reed-Sternberg cells. Additionally, it is positive in some peripheral T-cell lymphomas, leukemia, colorectal, lung, ovarian, peritoneal serous and renal cell carcinomas, and in mycosis fungoides, and it is a marker of poor prognosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia. It is also positive in papillary and medullary thyroid carcinoma, with higher positivity in anaplastic and conventional carcinoma over follicular variants. It may be a useful marker for malignant thyroid neoplasms as it does not typically stain benign thyroid tissues.
References: Endocr Pathol. 2016 Dec;27(4):271-275, PMID: 27550342; Leuk Res 2014;38:194, PMID: 24296270; Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry: Theranostic and Genomic Applications, 3rd Edition. 2011. Ch 6: 156-188, DOI: 10.1016/B978-1-4160-5766-6.00010-8; Mol Cell Biol. 2004 May;24(10):4221-8, PMID: 5121843
4 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(4)
Type
Primary
(4)
Target
SSEA-1 / Lewis x / CD15
(4)
Reactivity
Human
(4)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(4)
Flo
(2)
Func
(1)
ICC
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
mouse
(4)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(4)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(4)
Isotype
IgM
(2)
IgM,k
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(4)
Clone
AHN1.1
(1)
MC-480
(1)
MMA
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(4)
Publications
No
(4)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
SSEA-1 / Lewis x / CD15 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (AHN1.1) Antibody
Human
Flo, Func, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
SSEA-1 / Lewis x / CD15 Mouse anti-Mouse Monoclonal (MC-480) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
Flo, ICC, IF, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.1 ml/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
SSEA-1 / Lewis x / CD15 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal Antibody
Human
IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.05 ml/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
SSEA-1 / Lewis x / CD15 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (MMA) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.1 ml/$375
Viewing 1-4
of 4
product results










