Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM ROR1 Antibodies
ROR1 (neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor-related 1, NTRKR1) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates the growth of neurites in the central nervous system. ROR1 controls synapse formation in hippocampal neurons in complex with ROR2, and the degree of ROR1 expression dictates the number and length of axonal branches extended by neurons. ROR1 has also been found to be vital for the development of hearing and the inner ear in humans and mice. In cancer, ROR1 promotes invasion in ovarian carcinoma and is a potential target of antibody inhibition therapies, particularly since ROR1 has generally low (but not absent) expression in adult tissue. In immunohistochemistry, ROR1 has highest positive membranous staining in parathyroid tissue, pancreatic islets, and some areas of the duodenum, esophagus and stomach.
References: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 111 (48): 17266–71, PMID: 25411317; J Cell Sci. 2005 Jan 15;118(Pt 2):433-46, PMID: 15654020; Protein Cell. 2014 Jul; 5(7): 496–502, PMID: 24752542; Neuroscience. 2010 Feb 17;165(4):1261-74, PMID: 19958813; PNAS May 24, 2016 113 (21) 5993-5998, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1522512113; Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 15;23(12):3061-3071
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
ROR1
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(2)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-P
(3)
ELISA
(2)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
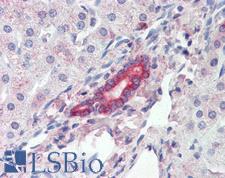
ROR1 Goat anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA
Unconjugated
50 µg/$485

Neuroscience
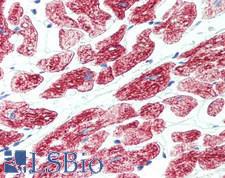
ROR1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
60 µl/$460

Neuroscience
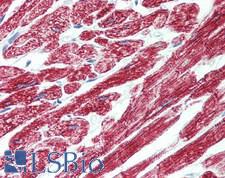
ROR1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
60 µl/$460
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











