Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM PTGS2 / COX2 / COX-2 Antibodies
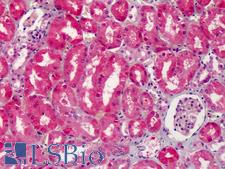
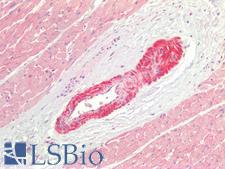
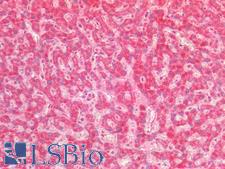
Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2 / PTGS2/ prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2) is an enzyme involved in the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2, a precursor of prostacyclin that is released during inflammation. Unlike COX1, which is constitutively expressed, COX2 is induced upon inflammation. COX2 is a frequent target for inhibitors (coxibs) to treat inflammatory conditions. Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents also inhibit prostaglandin and prostacyclin production by COX2. Overexpression of COX2 also occurs in many cancers, and COX2 inhibitors may assist in preventing the development of colorectal cancers. Staining for COX2 is expected to be cytoplasmic and potentially membranous. In normal tissues, it is expressed in a variety of cells including endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, cardiac myocytes, the brain and spinal cord, kidney, the GI tract, lung and bladder.
References: Biochem Soc Transact 2008 36(3):543; Nat Reviews Drug Discovery 2003 2:179; J Cell Phys 2019 234(5):5683; Gastroenterology 1994 107(4):1183, Curr Med Chem 2000 7(11):1113; PNAS 2016 113(2):434
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
PTGS2 / COX2 / COX-2
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Sheep
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(1)
ICC
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(3)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(3)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
aa550-600
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PTGS2 / COX2 / COX-2 Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa550-600) Antibody
Mouse, Sheep, Rat, Human
ICC, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
1 Each/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
PTGS2 / COX2 / COX-2 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
PTGS2 / COX2 / COX-2 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results










