Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
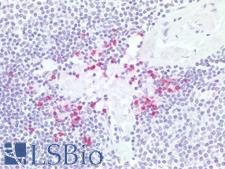
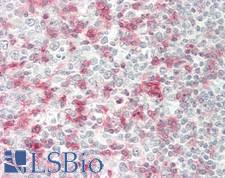
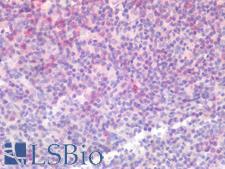
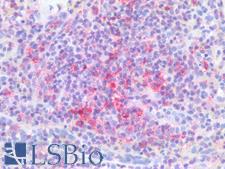
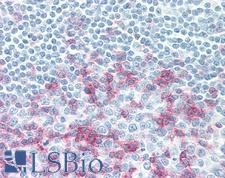
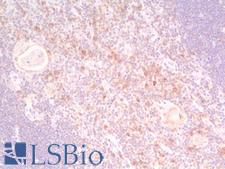
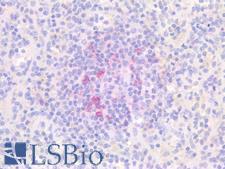
PathPlusTM PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1 Antibodies
PD1 (Programmed Death Receptor 1, PDCD1, CD279) is an immune checkpoint protein active in T cells that is a target alongside its ligand PDL1 and also CTLA-4 for immunotherapy in lung and other cancers. PD1 is involved in negatively regulating T cell inflammatory activity and, when bound to receptors on tumor cells, can work to subdue tumor suppression by inhibiting the immune response. Targeted inhibition of PD1 itself can therefore function as an anti-cancer therapy by reactivating this response. PD1 is expected to have membranous staining in germinal center associated helper T cells, CD8+ T cells, and Pro-B cells. It is for the identification of subsets of T and B cell lymphomas and nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphomas.
References: Alsaab, 2017; Jin, 2011; Francisco, 2010; Fife, 2011; Human Pathol 2008 39(7):1050
7 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(7)
Type
Primary
(7)
Target
PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1
(7)
Reactivity
Human
(7)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-P
(7)
WB
(2)
Flo
(3)
ELISA
(3)
ICC
(1)
IF
(2)
Host
rabbit
(1)
mouse
(6)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(7)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(7)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG1
(2)
IgG2a
(2)
IgG2b
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(6)
polyclonal pc
(1)
Clone
11B2
(1)
3C6
(1)
5D3
(1)
AHC0211
(1)
Format
Concentrated
(1)
Unconjugated
(7)
Epitope
Internal
(1)
Publications
No
(6)
Yes
(1)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (3C6) Antibody
Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (11B2) Antibody
Human
Flo, IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (5D3) Antibody
Human
ELISA, Flo, ICC, IF, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.1 mg/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Concentrated) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC-P
Unconjugated, Concentrated
0.05 ml/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
PDCD1 / CD279 / PD-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (AHC0211) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.1 ml/$375
Viewing 1-7
of 7
product results










