Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM NR6A1 / GCNF Antibodies
Germ cell nuclear factor (GCNF), a NR6 Germ Cell Nuclear Factor-Like Receptor, has been shown to affect gene expression in embryogenesis and spermatogenesis and is essential for embryonic survival and normal development. Loss of GCNF causes embryonic lethality and disrupts normal somitogenesis as well as neural-tube and axis formation. GCNF binds as a homodimer to the DR0 DNA response element and has been shown to regulate transcription of genes including protamines1 and 2 and Oct4. GCNF's repression function has been shown to be mediated by interaction with the co-repressors N-COR and SMRT in the absence of ligand. Three protein isoforms, GCNF-1, GCNF-2a, and GCNF-2b, have been documented in humans, and they are generated by differential usage of alternative splice acceptor sites of the fourth and seventh exons. GCNF-1, the longest isoform, has a distinct 5' UTR and contains 4 and 26 additional amino acids than the other two forms, respectively.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
NR6A1 / GCNF
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(2)
Bat
(2)
Bovine
(2)
Chicken
(1)
Dog
(2)
Hamster
(2)
Horse
(2)
Monkey
(2)
Pig
(2)
Rabbit
(2)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
Ligand-binding Domain
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Cancer
Fast Shipping
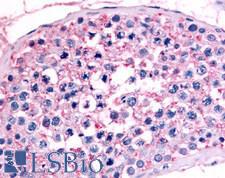
NR6A1 / GCNF Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Ligand-binding Domain) Antibody
Rabbit, Mouse, Dog, Bovine, Rat, Hamster, Pig, Horse, Bat, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer
Fast Shipping
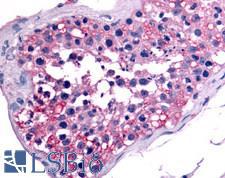
NR6A1 / GCNF Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Ligand-binding Domain) Antibody
Chicken, Bovine, Rat, Hamster, Pig, Horse, Bat, Rabbit, Mouse, Dog, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











