Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM NR5A2 / LRH-1 Antibodies
Alpha1-fetoprotein transcription factor (Ftf), a NR5 fushi tarazu-like receptor, also is known as 'human B1-binding factor' (HB1F), 'CYP7A promoter-binding factor' (CPF), and 'liver receptor homolog 1' (LRH1). Ftf has been shown to affect the transcription of hepatic genes including alpha fetoprotein encoding gene (AFP), viral hepatitis B enhancer II, and 7-alpha-hydroxylase encoding gene (CYP7A1). Ftf has also been shown to affect hepatic cholesterol metabolism and bile acid synthesis. Ftf has been shown to regulate aromatase activities in adipose tissue, and alterations in Ftf expression and/or activity in adipose tissue could have considerable effects on local estrogen production and breast cancer development. LRH has been shown to expressly strongly in gonadal tissues, and may play an important role in the regulation of gonadal function. Three isoforms of Ftf have been identified: wild type (495 aa), CPF variant 1 (contains a 46-aa insertion in the A/B domain), and CPF variant 2 (contains a 172-aa deletion within the D/E domain).
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
NR5A2 / LRH-1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Chicken
(1)
Dog
(2)
Hamster
(1)
Horse
(2)
Monkey
(2)
Pig
(1)
Sheep
(1)
Xenopus
(1)
Zebrafish
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Internal
(1)
Publications
No
(1)
Yes
(1)

Cancer
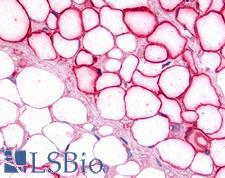
NR5A2 / LRH-1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Dog, Sheep, Bovine, Pig, Horse, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer
Fast Shipping
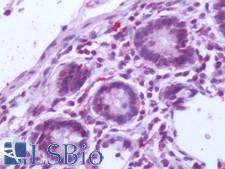
NR5A2 / LRH-1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Xenopus, Chicken, Zebrafish, Horse, Rat, Hamster, Mouse, Dog, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











