Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM NEFM / NF-M Antibodies
NEFM is an intermediate filament component of the neurofilament heteropolymers that form the neuronal cytoskeleton together with microtubules. Neurofilaments act as structural space-fillers for axons and are also involved in axonal transport. Antibodies that detect NEFM are regularly used to identify neurons and distinguish them from glia (neurofilament-negative) and for diagnosis in neuropathology. Because neurofilaments are released into the blood when axons and neurons deteriorate, antibodies to neurofilaments are also used to observe the progression and state of neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis and Huntington’s disease, and NEFM is a common biomarker of neuronal damage. In immunohistochemistry, NEFM antibodies highlight axons of neuronal cells in the central nervous system and in peripheral nerves.
References: European Journal of Neurology. 2010 Mar. 17 (3): 377–8, PMID: 19845747; Neurology. 2009 Apr. 72 (15): 1322–9, PMID: 19365053; PLOS One. 2017 Feb. 12 (2): e0172762, PMID: 28241046; Garland Science. ISBN: 978-0-8153-3218-3.
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
NEFM / NF-M
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Guinea pig
(1)
Hamster
(3)
Horse
(1)
Monkey
(3)
Pig
(1)
Rabbit
(2)
Xenopus
(2)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-Fr
(2)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(3)
Flo
(1)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
mouse
(2)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Isotype
IgG1
(2)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(2)
polyclonal pc
(1)
Clone
RNF403
(1)
RNF406
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
aa250-263
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
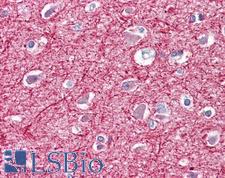
NEFM / NF-M Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (RNF406) Antibody
Xenopus, Hamster, Rabbit, Guinea pig, Human, Monkey
Flo, IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.05 mg/$460

Neuroscience
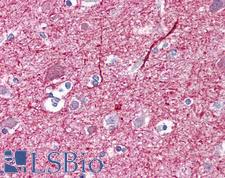
NEFM / NF-M Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (RNF403) Antibody
Xenopus, Hamster, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.05 mg/$375

Neuroscience
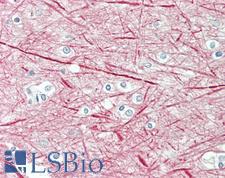
NEFM / NF-M Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa250-263) Antibody
Rabbit, Mouse, Dog, Bovine, Rat, Hamster, Pig, Horse, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$485
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results










