Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM MKI67 / Ki67 Antibodies
Ki-67 (MKI67) protein is a marker for proliferation commonly used in breast cancer pathology. It can be used to determine the growth fraction of cell populations in many tumors and tissue types. In the brain, it can be used to estimate rates of neurogenesis and aging-related neurogenerative decline. In breast cancer, the degree of expression of Ki-67 is used in conjunction with ER, PR and HER2 expression levels to subtype breast cancers. Higher levels of this protein are correlated with increased rates of proliferation (Zaha, 2014), absence of ER and PR and poor prognosis, and staining for Ki-67 in immunohistochemistry is thus important for determining the necessary treatment (Zorka, 2014). In normal tissues, Ki-67 has positive nuclear staining throughout the body, with strongest staining in germinal center cells and in subsets of cells in seminiferous ducts, squamous epithelia and the gastrointestinal tract.
References: World Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2014. 5.3; 382-392, PMID: 25114853; Oncology 2014 Sep; 8; 107-111, PMID: 25249766; Aging Cell. 2017 Oct;16(5):1195-1199, PMID: 28766905; Int J Cancer 1983;31:13, PMID: 6339421;
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
MKI67 / Ki67
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Pig
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(2)
ELISA
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
mouse
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(3)
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG1
(1)
IgG2b
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(2)
polyclonal pc
(1)
Clone
19
(1)
AHC0157
(1)
Format
Preservative Free
(1)
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
aa1550-1700
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
Cancer Pathology
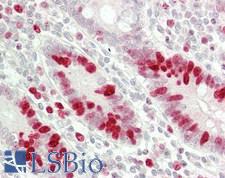
MKI67 / Ki67 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa1550-1700) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Pig, Human
IF, IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.1 ml/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
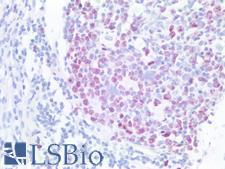
MKI67 / Ki67 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (AHC0157) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Neuroscience
Cancer Pathology
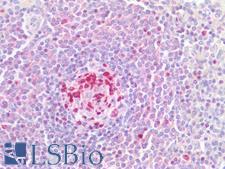
MKI67 / Ki67 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Preservative Free) (19) Antibody
Human
IHC-P
Unconjugated, Preservative Free
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











