Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM MAPT / Tau Antibodies
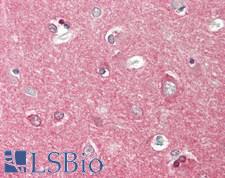
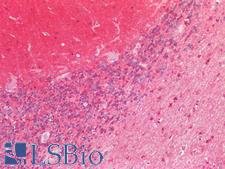
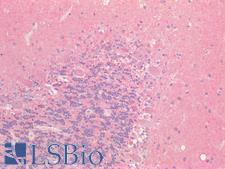
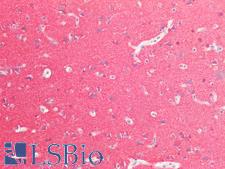
Tau proteins are microtubule-associated proteins transcribed from the MAPT gene. They promote microtubule assembly and stability, and might be involved in the establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. In Alzheimer’s disease, the neuronal cytoskeleton in the brain is progressively disrupted and replaced by tangles of paired helical filaments (PHF) and straight filaments, mainly composed of hyperphosphorylated forms of TAU. Abnormal quantities of Tau protein in neurons and sometimes astrocytes are also seen in progressive supranuclear palsy. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, Tau has positive cytoplasmic staining in the central nervous system, renal tubules and in peripheral nerves, with some expression in other tissues including skeletal muscle, kidney and breast.
References: J Mol Biol. 2016 May 8;428(9 Pt A):1742-59, PMID: 26996940; PNAS. 2015 June. 112 (24) 7501-7506, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1504081112; Acta Neuropathol. 1991;81(6):591-6, PMID: 1831952
5 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(5)
Type
Primary
(5)
Target
MAPT / Tau
(5)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(3)
Rat
(2)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(5)
WB
(3)
ELISA
(1)
ICC
(1)
IF
(1)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(4)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(3)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(5)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG1
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(4)
Clone
MCA-2E9
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(5)
Epitope
aa463-512
(1)
Publications
No
(5)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
MAPT / Tau Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (MCA-2E9) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
ICC, IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
MAPT / Tau Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa463-512) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
MAPT / Tau Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Human
ELISA, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µg/$375

Cancer Pathology
Fast Shipping
MAPT / Tau Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer Pathology
Fast Shipping
MAPT / Tau Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-5
of 5
product results











