Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM MAP2 Antibodies
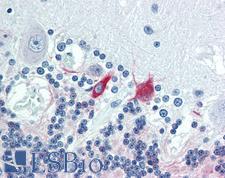
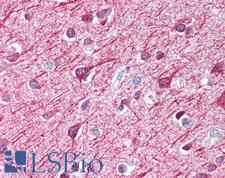
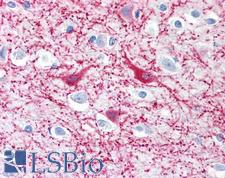
MAP2 (Microtubule-associated protein 2) is a member of the microtubule-associated protein family. These proteins are involved in microtubule assembly, essential for neurogenesis. They may be involved in controlling and supporting dentritic shape in developing neurons. In immunohistochemistry, MAP2 is a useful marker of neurons (glial precursor cells) and neuronal differentiation and shows cytoplasmic positivity. It is also used in the differential diagnosis of a number of diseases. For example, Hirschsprung’s disease is described by loss of MAP2 versus normal tissue. In ischemic stroke, it may be used to measure infarct volume. In neuroepithelial tumors, it distinguishes oligodendrogliomas and astrocytomas (positive) from dysembryoplastic tumors and the clear cell component of neurocytomas (negative). Finally, it may be a useful marker of prognosis in melanoma, as MAP2 positivity correlates with survival.
References: Histopathology. 2015 May;66(6):824-35, PMID: 25123159; Epilepsy Res Treat. 2012; 2012: 624519, PMID: 22957233; Am J Pathol. 2005 Jun; 166(6): 1841–1850, PMID: 15920168; J Neurosci Methods. 2009 Sep 15;182(2):205-10, PMID: 19540877; J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2001 Oct;60(10):984-93, PMID: 11589429
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
MAP2
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Mouse
(3)
Rat
(2)
Bovine
(1)
Porcine
(1)
Rabbit
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(2)
ELISA
(1)
ICC
(1)
IP
(1)
Host
mouse
(2)
chicken
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(3)
Isotype
IgG1
(2)
IgY
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(2)
polyclonal pc
(1)
Clone
5F9
(1)
MT-07
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Publications
Yes
(2)
No
(1)

Cancer
MAP2 Mouse anti-Rat Monoclonal (5F9) Antibody
Rabbit, Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$675

Cancer
MAP2 Chicken anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Bovine, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.05 ml/$375

Cancer
MAP2 Mouse anti-Bovine Monoclonal (MT-07) Antibody
Mouse, Porcine, Human
ELISA, ICC, IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











