Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
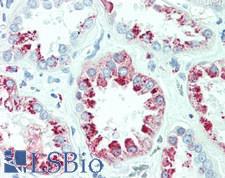
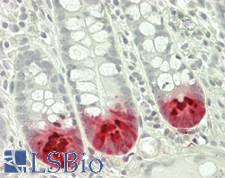
PathPlusTM LYZ / Lysozyme Antibodies
Lysozyme (Muramidase, LYZ) is a bacteriolytic and histiocytic enzyme that functions in the immune system as a defense mechanism against certain pathogens. Lysozyme can break down the peptidoglycans that compose gram-positive bacterial cell walls (such as Streptococcus and Bacillus). High levels of lysozyme are present in egg white, and in humans it is found in secreted mucus, tears, saliva, and milk. It is also expressed in macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. In immunohistochemistry, lysozyme stains positively in histiocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, goblet cells, lactating lobules of the breast, some epithelial cells and normal hematopoietic cells. In cancer, it is positive in myeloid leukemias where it can by highly overexpressed, acinic cell carcinomas of the breast and salivary gland, goblet cell carcinoids, myeloid sarcomas and various histiocytic lesions.
References: Am J Surg Pathol. 2009. 33:1137, PMID: 19461506; CRC Press. 1994. p. 223. ISBN: 978-0-8493-8935-1; McGraw-Hill Higher Education. 2007. ISBN: 978-0-07-110706-8; Am J Clin Pathol. 1992 Feb;97(2):195-201, PMID: 1546687
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
LYZ / Lysozyme
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
Flo
(2)
ELISA
(1)
Host
mouse
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(2)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(2)
Isotype
IgG1
(1)
IgG2a
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(2)
Clone
BGN/0696/5B1
(1)
LZ-2
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
LYZ / Lysozyme Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (BGN/0696/5B1) Antibody
Human
ELISA, Flo, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
0.1 mg/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
LYZ / Lysozyme Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (LZ-2) Antibody
Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µg/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











